Vanoxerine
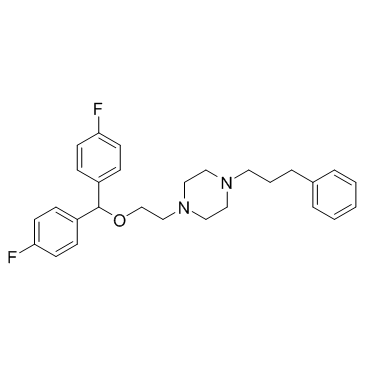
Vanoxerine structure
|
Common Name | Vanoxerine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 67469-69-6 | Molecular Weight | 450.56300 | |
| Density | 1.135g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 542.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H32F2N2O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 282ºC | |
Use of VanoxerineVanoxerine (GBR12909) is a potent and selective DRI (Dopamine reuptake inhibitor).IC50 value:Target: Dopamine reuptake inhibitorAt a cellular level, vanoxerine acts to block cardiac ion channels. Vanoxerine is a multichannel blocker, acting on IKr (potassium), L-type calcium and sodium ion channels.[14] By blocking these specific channels, there is a prolongation of the action potential of the cell, preventing reactivation by a reentrant circuit. The block is strongly frequency dependant: as the pacing of the heart increases so does the frequency of ion channel blocking by vanoxerine. Vanoxerine is a potentially effective treatment for cardiac arrhythmias. A significant cause of cardiac arrhythmias is reentry, an electrophysiologic event in which the proliferating signal that refuses to terminate, and endures to reexcite the heart after the refractory period. |
| Name | vanoxerine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Vanoxerine (GBR12909) is a potent and selective DRI (Dopamine reuptake inhibitor).IC50 value:Target: Dopamine reuptake inhibitorAt a cellular level, vanoxerine acts to block cardiac ion channels. Vanoxerine is a multichannel blocker, acting on IKr (potassium), L-type calcium and sodium ion channels.[14] By blocking these specific channels, there is a prolongation of the action potential of the cell, preventing reactivation by a reentrant circuit. The block is strongly frequency dependant: as the pacing of the heart increases so does the frequency of ion channel blocking by vanoxerine. Vanoxerine is a potentially effective treatment for cardiac arrhythmias. A significant cause of cardiac arrhythmias is reentry, an electrophysiologic event in which the proliferating signal that refuses to terminate, and endures to reexcite the heart after the refractory period. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.135g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 542.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C28H32F2N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 450.56300 |
| Flash Point | 282ºC |
| Exact Mass | 450.24800 |
| PSA | 15.71000 |
| LogP | 5.19700 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.561 |
| InChIKey | NAUWTFJOPJWYOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Fc1ccc(C(OCCN2CCN(CCCc3ccccc3)CC2)c2ccc(F)cc2)cc1 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
|
~% 
Vanoxerine CAS#:67469-69-6 |
| Literature: Organic Process Research and Development, , vol. 6, # 5 p. 621 - 627 |
|
~% 
Vanoxerine CAS#:67469-69-6 |
| Literature: Organic Process Research and Development, , vol. 6, # 5 p. 621 - 627 |
|
~% 
Vanoxerine CAS#:67469-69-6 |
| Literature: Organic Process Research and Development, , vol. 6, # 5 p. 621 - 627 |
|
~% 
Vanoxerine CAS#:67469-69-6 |
| Literature: Organic Process Research and Development, , vol. 6, # 5 p. 621 - 627 |
| Vanoxerinum |
| Vanoxerina |
| 1-[2-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methoxy]ethyl]-4-(3-phenylpropyl)piperazine |
| Vanoxerine |

![1-[2-chloroethoxy-(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-fluorobenzene structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/391/50366-31-9.png)