N-ω-Acetylhistamine
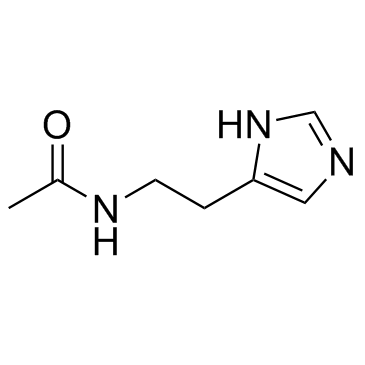
N-ω-Acetylhistamine structure
|
Common Name | N-ω-Acetylhistamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 673-49-4 | Molecular Weight | 153.18200 | |
| Density | 1.153g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 501.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H11N3O | Melting Point | 147-149ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 257.2ºC | |
Use of N-ω-AcetylhistamineN-acetylhistamine is a histamine metabolite. N-acetylhistamine can be used as a potential biomarker of histidine metabolism for anaphylactoid reactions. |
| Name | N-acetylhistamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N-acetylhistamine is a histamine metabolite. N-acetylhistamine can be used as a potential biomarker of histidine metabolism for anaphylactoid reactions. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | N-acetylhistamine is an important indice for anaphylactoid reactions[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.153g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 501.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 147-149ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H11N3O |
| Molecular Weight | 153.18200 |
| Flash Point | 257.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 153.09000 |
| PSA | 57.78000 |
| LogP | 0.47920 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.533 |
| InChIKey | XJWPISBUKWZALE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=O)NCCc1cnc[nH]1 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2933290090 |
|
~% 
N-ω-Acetylhistamine CAS#:673-49-4 |
| Literature: Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschrift fuer Physiologische Chemie, , vol. 177, p. 305 |
| HS Code | 2933290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933290090. other compounds containing an unfused imidazole ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
[Oscillographic polarography of the alkaloid dolicotheline and several related imidazole derivatives].
Farmakol. Toksikol. 44(2) , 220-4, (1981) Oscillographic polarography in an alkaline medium has shown that the alkaloid N-isovalerylhistamine appears as an expressive wave of the adsorption character in the cathode portion of the curve. This ... |
|
|
Monooxygenation of N-acetylhistamine mediated by L-ascorbate.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 991(2) , 377-9, (1989) In the presence of molecular oxygen and a catalytic amount of copper(II) ion, ascorbate almost completely degraded histamine (approx. 72%). The reaction was shown to occur at the imidazole group but n... |
|
|
Effects of intracerebroventricular administration of N-acetylhistamine on body temperature in mice.
Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 16(8) , 575-81, (1994) The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of N-acetylhistamine on rectal temperature, histamine level, histidine decarboxylase (HDC) activ... |
| EINECS 211-610-3 |
| Nomega-Acetylhistamine |
| N'-Acetylhistamine |
| N-[2-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)ethyl]acetamide |
| N-[2-(1H-Imidazol-4-yl)ethyl]acetamide |
| MFCD00005209 |
| 4-(2-acetamidoethyl)imidazole |
| Nw-acetyl-histamine |
| Acetylhistamine |
| N-ω-Acetylhistamine |

 CAS#:39050-13-0
CAS#:39050-13-0![N-[2-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-imidazol-5-yl]ethyl]acetamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/209/88181-33-3.png) CAS#:88181-33-3
CAS#:88181-33-3![N-[2-[4-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-imidazol-5-yl]ethyl]acetamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/057/88181-37-7.png) CAS#:88181-37-7
CAS#:88181-37-7![N-[2-[2,4-bis(trifluoromethyl)-1H-imidazol-5-yl]ethyl]acetamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/078/88181-41-3.png) CAS#:88181-41-3
CAS#:88181-41-3 CAS#:501-75-7
CAS#:501-75-7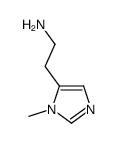 CAS#:644-42-8
CAS#:644-42-8
