auriculasin
Modify Date: 2025-08-23 21:41:27
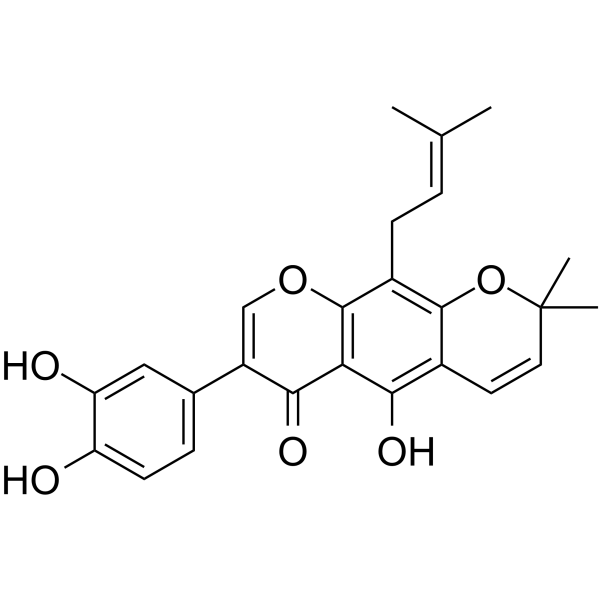
auriculasin structure
|
Common Name | auriculasin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 60297-37-2 | Molecular Weight | 420.45 | |
| Density | 1.314g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 668ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H24O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 231.2ºC | |
Use of auriculasinAuriculasin is a nature product isolated from Limonium leptophyllum. Auriculasin has activity toward cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) with an IC50 value of 8.92 µM[1]. |
| Name | 7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-10-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)pyrano[3,2-g]chromen-6-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Auriculasin is a nature product isolated from Limonium leptophyllum. Auriculasin has activity toward cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) with an IC50 value of 8.92 µM[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
CB1:8.92 μM (IC50) |
| References |
| Density | 1.314g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 668ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C25H24O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 420.45 |
| Flash Point | 231.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 420.15700 |
| PSA | 100.13000 |
| LogP | 5.26970 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.644 |
| InChIKey | PSEBCAMYGWGJMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C)=CCc1c2c(c(O)c3c(=O)c(-c4ccc(O)c(O)c4)coc13)C=CC(C)(C)O2 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
|
~90% 
auriculasin CAS#:60297-37-2 |
| Literature: Barua, P.; Barua, N. C.; Sharma, R.P. Tetrahedron Letters, 1983 , vol. 24, # 51 p. 5801 - 5804 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| 7-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-10-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-2H,6H-pyrano[3,2-g]chromen-6-one |
| AURICULASIN |
| 2H,6H-Benzo[1,2-b:5,4-b']dipyran-6-one, 7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-10-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)- |
| auriculatin |
