Dithizone
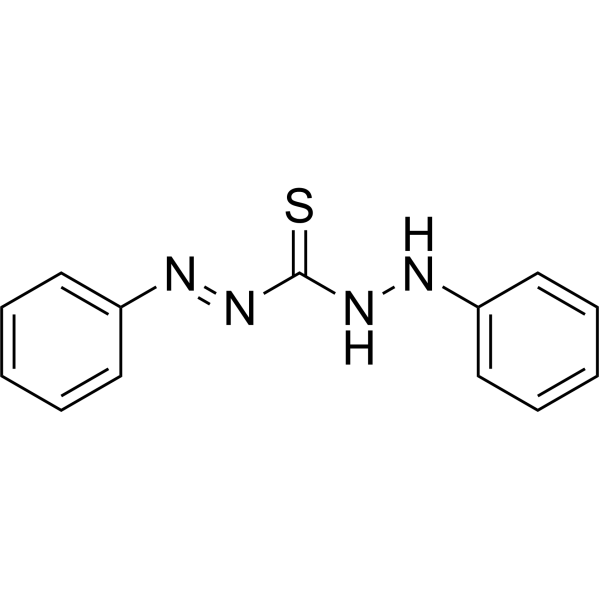
Dithizone structure
|
Common Name | Dithizone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 60-10-6 | Molecular Weight | 256.33 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 376.1±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H12N4S | Melting Point | 168°C (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 181.2±23.2 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of DithizoneDithizone,for analysis (Diphenylthiocarbazone) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
| Name | Diphenylthiocarbazone |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dithizone,for analysis (Diphenylthiocarbazone) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 376.1±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 168°C (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C13H12N4S |
| Molecular Weight | 256.33 |
| Flash Point | 181.2±23.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 256.078278 |
| PSA | 80.87000 |
| LogP | 4.01 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.644 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S36-S26 |
| RIDADR | 2811 |
| RTECS | LQ9450000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 8 | |
|
Immunotoxicity in ascidians: antifouling compounds alternative to organotins-IV. The case of zinc pyrithione.
Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 169 , 16-24, (2015) New biocides such as the organometallic compound zinc pyrithione (ZnP) have been massively introduced by many countries in formulations of antifouling paints following the ban on tributyltin (TBT). Th... |
|
|
Long-term survival of allograft murine islets coated via covalently stabilized polymers.
Adv. Healthc. Mater. 3(7) , 1061-70, (2014) Clinical islet transplantation (CIT) has emerged as a promising treatment option for type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM); however, the antirejection drug regimen necessary to mitigate allograft islet reje... |
|
|
Feasibility of islet magnetic resonance imaging using ferumoxytol in intraportal islet transplantation.
Biomaterials 52 , 272-80, (2015) There is a clinical need for an alternative labeling agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in islet transplantation. We aimed to evaluate the feasibility of islet MRI using ferumoxytol, which is ... |
| (E)-N',2-Diphenyldiazenecarbothiohydrazide |
| Methanethione, [(E)-2-phenyldiazenyl](2-phenylhydrazinyl)- |
| Dithizone |
| Phenyldiazenecarbothioic Acid 2-Phenylhydrazide |
| MFCD00003025 |
| diphenylthiocarbazone |
| EINECS 200-454-1 |
 CAS#:100-63-0
CAS#:100-63-0 CAS#:50878-38-1
CAS#:50878-38-1 CAS#:4453-80-9
CAS#:4453-80-9 CAS#:622-03-7
CAS#:622-03-7 CAS#:2684-02-8
CAS#:2684-02-8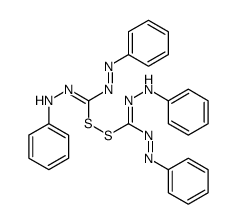 CAS#:25210-27-9
CAS#:25210-27-9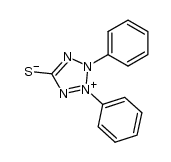 CAS#:11065-31-9
CAS#:11065-31-9 CAS#:67-64-1
CAS#:67-64-1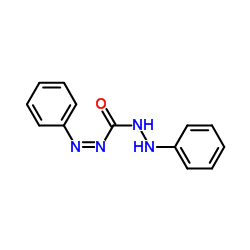 CAS#:538-62-5
CAS#:538-62-5 CAS#:645-48-7
CAS#:645-48-7![Benzo[d]thiazol-2-amine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/040/136-95-8.png) CAS#:136-95-8
CAS#:136-95-8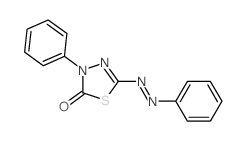 CAS#:17883-57-7
CAS#:17883-57-7 CAS#:17883-56-6
CAS#:17883-56-6 CAS#:51808-07-2
CAS#:51808-07-2
