4-cumylphenol
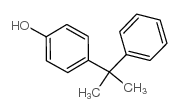
4-cumylphenol structure
|
Common Name | 4-cumylphenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 599-64-4 | Molecular Weight | 212.28700 | |
| Density | 1,115 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 335 °C | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H16O | Melting Point | 72-75 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 160 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 4-cumylphenol4-Cumylphenol is a polycarbonate chain terminator. 4-Cumylphenol is widely used as a material for polycarbonate plastics, surfactants, fungicides and preservatives. 4-Cumylphenol also induces lipid accumulation in mouse adipocytes[1][2][3]. |
| Name | 4-cumylphenol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 4-Cumylphenol is a polycarbonate chain terminator. 4-Cumylphenol is widely used as a material for polycarbonate plastics, surfactants, fungicides and preservatives. 4-Cumylphenol also induces lipid accumulation in mouse adipocytes[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | 4-Cumylphenol (1, 5, 10, 20, 40 µM; 6 days) increase lipid accumulation in 3 T3-L1 cells[3]. Cell Viability Assay[3] Cell Line: 3 T3-L1 cells Concentration: 1, 5, 10, 20, 40 µM Incubation Time: 6 days Result: Increase lipid accumulation, which peaked at10 μM with a 204% increase. |
| References |
| Density | 1,115 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 335 °C |
| Melting Point | 72-75 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C15H16O |
| Molecular Weight | 212.28700 |
| Flash Point | 160 °C |
| Exact Mass | 212.12000 |
| PSA | 20.23000 |
| LogP | 3.71810 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.587 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides. Combustible. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25-S37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | SL1942450 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
|
Degradation and toxicity reduction of the endocrine disruptors nonylphenol, 4-tert-octylphenol and 4-cumylphenol by the non-ligninolytic fungus Umbelopsis isabellina.
Bioresour. Technol. 200 , 223-9, (2015) Nonylphenol (NP), 4-tert-octylphenol (4-t-OP) and 4-cumylphenol (4-CP) are pollutants that are known as endocrine disruptors mainly due to their estrogen-mimicking activity. These phenolic substances ... |
|
|
Occurrence, removal, and fate of progestogens, androgens, estrogens, and phenols in six sewage treatment plants around Dianchi Lake in China.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 21(22) , 12898-908, (2014) The occurrence and behavior of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in sewage treatment plants (STPs), especially estrogens and phenols, have been closely concerned in previous studies. However, the ... |
|
|
Double salts of ionic-liquid-based surfactants in microextraction: application of their mixed hemimicelles as novel sorbents in magnetic-assisted micro-dispersive solid-phase extraction for the determination of phenols.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407 , 8753-64, (2015) The use of mixed hemimicelles of ionic liquid (IL)-based surfactants in a magnetic-based micro-dispersive solid-phase extraction (m-μdSPE) approach is described. Not only is the symmetric monocationic... |
| P-CUMYLPHENOL |
| AURORA 4778 |
| paracumilphenol |
| PARA-CUMYLPHENOL |
| PCP |
| Cumyl phenol |
| EINECS 209-968-0 |
| MFCD00002365 |
 CAS#:80-05-7
CAS#:80-05-7 CAS#:98-83-9
CAS#:98-83-9 CAS#:108-95-2
CAS#:108-95-2 CAS#:617-94-7
CAS#:617-94-7 CAS#:6623-93-4
CAS#:6623-93-4 CAS#:934-53-2
CAS#:934-53-2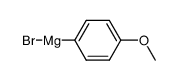 CAS#:13139-86-1
CAS#:13139-86-1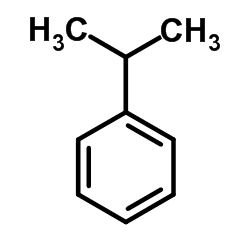 CAS#:98-82-8
CAS#:98-82-8 CAS#:80-15-9
CAS#:80-15-9 CAS#:20056-52-4
CAS#:20056-52-4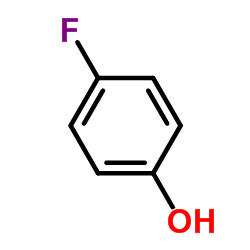 CAS#:371-41-5
CAS#:371-41-5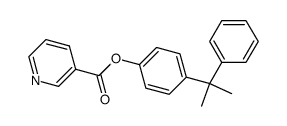 CAS#:76953-23-6
CAS#:76953-23-6 CAS#:628-13-7
CAS#:628-13-7 CAS#:24133-73-1
CAS#:24133-73-1 CAS#:24133-64-0
CAS#:24133-64-0![4-[4-(2-Phenyl-2-propanyl)phenoxy]phthalonitrile structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/224/83482-57-9.png) CAS#:83482-57-9
CAS#:83482-57-9 CAS#:33524-49-1
CAS#:33524-49-1 CAS#:119-36-8
CAS#:119-36-8
