| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
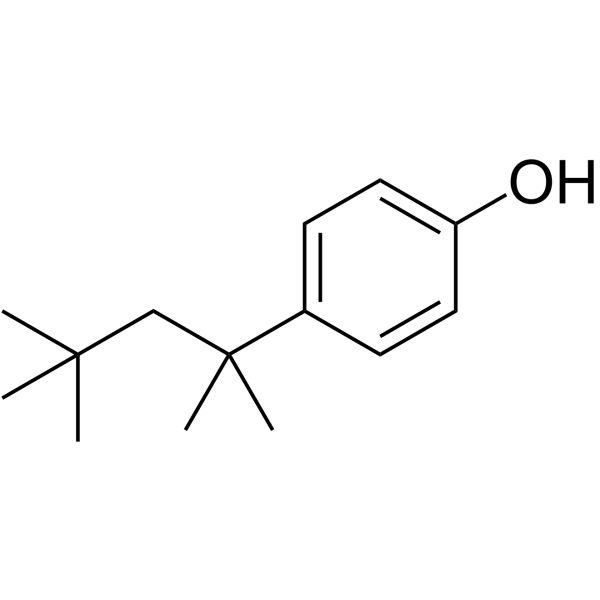 |
4-tert-Octylphenol
CAS:140-66-9 |
|
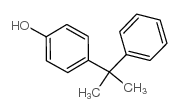 |
4-cumylphenol
CAS:599-64-4 |
|
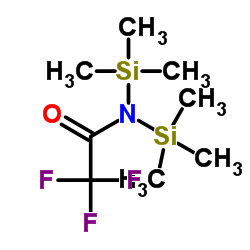 |
bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide
CAS:25561-30-2 |
|
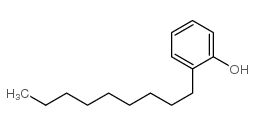 |
4-Nonylphenol, branched
CAS:84852-15-3 |