N-Nitrosodiethylamine
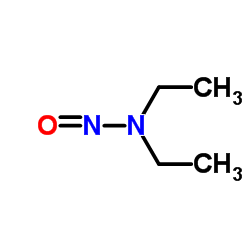
N-Nitrosodiethylamine structure
|
Common Name | N-Nitrosodiethylamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 55-18-5 | Molecular Weight | 102.135 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 173.9±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H10N2O | Melting Point | <25℃ | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 59.0±18.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of N-NitrosodiethylamineN-Nitrosodiethylamine is a potent hepatocarcinogenic dialkylnitrosoamine. N-Nitrosodiethylamine is mainly present in tobacco smoke, water, cheddar cheese, cured, fried meals and many alcoholic beverages. N-Nitrosodiethylamine is responsible for the changes in the nuclear enzymes associated with DNA repair/replication. N-Nitrosodiethylamine results in various tumors in all animal species. The main target organs are the nasal cavity, trachea, lung, esophagus and liver. |
| Name | N-nitrosodiethylamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N-Nitrosodiethylamine is a potent hepatocarcinogenic dialkylnitrosoamine. N-Nitrosodiethylamine is mainly present in tobacco smoke, water, cheddar cheese, cured, fried meals and many alcoholic beverages. N-Nitrosodiethylamine is responsible for the changes in the nuclear enzymes associated with DNA repair/replication. N-Nitrosodiethylamine results in various tumors in all animal species. The main target organs are the nasal cavity, trachea, lung, esophagus and liver. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 173.9±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | <25℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C4H10N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 102.135 |
| Flash Point | 59.0±18.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 102.079315 |
| PSA | 32.67000 |
| LogP | 0.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.7±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.442 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable, but light sensitive. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, reducing agents. |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 + H311 + H331-H350-H370 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P260-P280-P301 + P310-P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T,F |
| Risk Phrases | 45-22-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45-S36/37-S16 |
| RIDADR | UN 2810 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | IA3500000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
|
The Japanese toxicogenomics project: application of toxicogenomics.
Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 54 , 218-27, (2010) Biotechnology advances have provided novel methods for the risk assessment of chemicals. The application of microarray technologies to toxicology, known as toxicogenomics, is becoming an accepted appr... |
|
|
Novel study on N-nitrosamines as risk factors of cardiovascular diseases.
Biomed Res. Int. 2014 , 817019, (2014) Millions of people are exposed daily to N-nitrosamines from different environmental sources. The present study aims at investigating the role of N-nitrosamines in the alteration of homocysteine, lipid... |
|
|
Genetic targeting of sprouting angiogenesis using Apln-CreER.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 6020, (2015) Under pathophysiological conditions in adults, endothelial cells (ECs) sprout from pre-existing blood vessels to form new ones by a process termed angiogenesis. During embryonic development, Apelin (A... |
| MFCD00013890 |
| Ethanamine, N-ethyl-N-nitroso- |
| DENA |
| Nitrosodiethylamine |
| Diethylnitrosoamine |
| N,N-Diethylnitrosoamine |
| Diethylamine,N-nitroso |
| NDEA |
| Diethylnitrosamine |
| EINECS 200-226-1 |
| N-nitroso-diethylamine |
| N,N-diethylnitrous amide |
| Ethanamine,N-ethyl-N-nitroso |
| N-Nitrosodiethylamine |
| N-Ethyl-N-nitrosoethanamine |

