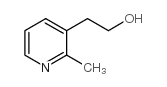
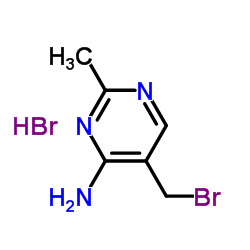
NEOPYRITHIAMINE HYDROBROMIDE
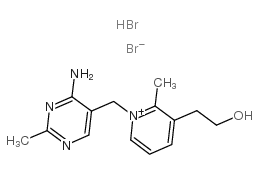
NEOPYRITHIAMINE HYDROBROMIDE structure
|
Common Name | NEOPYRITHIAMINE HYDROBROMIDE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 534-64-5 | Molecular Weight | 420.14300 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H20Br2N4O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of NEOPYRITHIAMINE HYDROBROMIDEPyrithiamine hydrobromide is the pyridine analog of thiamine that prevents growth of organisms that require intact thiamine. |
| Name | Pyrithiamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Molecular Formula | C14H20Br2N4O |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 420.14300 |
| Exact Mass | 418.00000 |
| PSA | 75.91000 |
| Appearance of Characters | crystalline | off-white to yellow |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
|
~% 
NEOPYRITHIAMINE... CAS#:534-64-5 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 71, p. 2231 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Interactions between chronic ethanol consumption and thiamine deficiency on neural plasticity, spatial memory, and cognitive flexibility.
Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 39 , 2143-53, (2015) Many alcoholics display moderate to severe cognitive dysfunction accompanied by brain pathology. A factor confounded with prolonged heavy alcohol consumption is poor nutrition, and many alcoholics are... |
|
|
Identification of the antiphagocytic trypacidin gene cluster in the human-pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99 , 10151-61, (2015) The opportunistic human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus produces numerous different natural products. The genetic basis for the biosynthesis of a number of known metabolites has remained unknown. The g... |
|
|
Thiamine deficiency caused by thiamine antagonists triggers upregulation of apoptosis inducing factor gene expression and leads to caspase 3-mediated apoptosis in neuronally differentiated rat PC-12 cells.
Acta Biochim. Pol. 54(2) , 315-22, (2007) Recent evidence suggests that alterations in oxidative metabolism induced by thiamine deficiency lead to neuronal cell death. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying this process are still under ... |
| neopyrithiamine hydrobromide |