Urethane
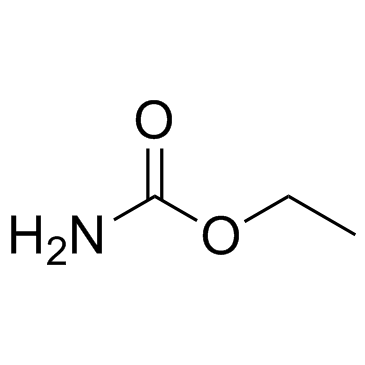
Urethane structure
|
Common Name | Urethane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 51-79-6 | Molecular Weight | 89.093 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 105.7±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO2 | Melting Point | 48-50 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 17.7±22.6 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of UrethaneUrethane has been used as an antineoplastic agent and for other medicinal purposes |
| Name | urethane |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Urethane has been used as an antineoplastic agent and for other medicinal purposes |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 105.7±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 48-50 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 89.093 |
| Flash Point | 17.7±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 89.047676 |
| PSA | 52.32000 |
| LogP | 0.07 |
| Vapour density | 3.07 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 15.9±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.423 |
| InChIKey | JOYRKODLDBILNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCOC(N)=O |
| Storage condition | Room temperature. |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H350 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P301 + P312 + P330-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic |
| Risk Phrases | R45 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN3077 9/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | FA8400000 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Mechanistic basis of altered morphine disposition in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 352(3) , 462-70, (2015) Morphine is metabolized in humans to morphine-3-glucuronide (M3G) and the pharmacologically active morphine-6-glucuronide (M6G). The hepatobiliary disposition of both metabolites relies upon multidrug... |
|
|
Loss of presenilin 2 is associated with increased iPLA2 activity and lung tumor development.
Oncogene 33(44) , 5193-200, (2014) Presenilins are the enzymatic components of γ-secretase complex that cleaves amyloid precursor protein, Notch and β-catenin, which has critical roles in the development of Alzheimer's disease and canc... |
|
|
The Ca²⁺-calmodulin-Ca²⁺/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II signaling pathway is involved in oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial permeability transition and apoptosis in isolated rat hepatocytes.
Arch. Toxicol. 88(9) , 1695-709, (2014) Oxidative stress (OS) is a common event in most hepatopathies, leading to mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) formation and further exacerbation of both OS from mitochondrial origin and ... |
| Ethyl urethane |
| urethane |
| Ethyl Carbamate |
| caproic acid ethyl ester |
| Carbamic Acid Ethyl Ester |
| Capronic ether absolute |
| 2-Ethyl Hexanoate |
| ethyl carbaminate |
| ethyl n-heptanoate |
| Carbamate, Ethyl |
| Ethyl hexoate |
| Carbamic acid, ethyl ester |
| Ethyl caproate |
| EINECS 200-123-1 |
| Ethyl urethan |
| Carbamic acid, ethyl ester (8CI 9CI) |
| methyl,methyl carbamate |
| MFCD00007966 |
| ethyl ester of carbamic acid |
| Hexanoic acid,ethyl ester |
| ethyl capronate |
 CAS#:64-17-5
CAS#:64-17-5 CAS#:57-13-6
CAS#:57-13-6 CAS#:60-29-7
CAS#:60-29-7 CAS#:2746-25-0
CAS#:2746-25-0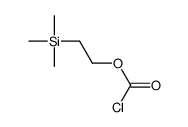 CAS#:20160-60-5
CAS#:20160-60-5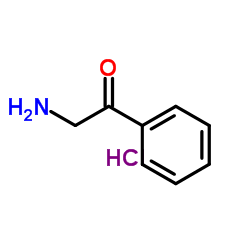 CAS#:5468-37-1
CAS#:5468-37-1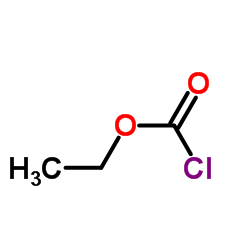 CAS#:541-41-3
CAS#:541-41-3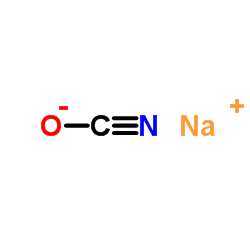 CAS#:917-61-3
CAS#:917-61-3 CAS#:624-83-9
CAS#:624-83-9 CAS#:100-39-0
CAS#:100-39-0 CAS#:538-32-9
CAS#:538-32-9 CAS#:3693-53-6
CAS#:3693-53-6 CAS#:141-83-3
CAS#:141-83-3 CAS#:90915-45-0
CAS#:90915-45-0 CAS#:1769-24-0
CAS#:1769-24-0![Carbamic acid, [(4-methoxyphenyl)methylene]bis-, diethyl ester (9CI) structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/290/21191-28-6.png) CAS#:21191-28-6
CAS#:21191-28-6 CAS#:2114-15-0
CAS#:2114-15-0 CAS#:18731-19-6
CAS#:18731-19-6
