Octanedioic acid
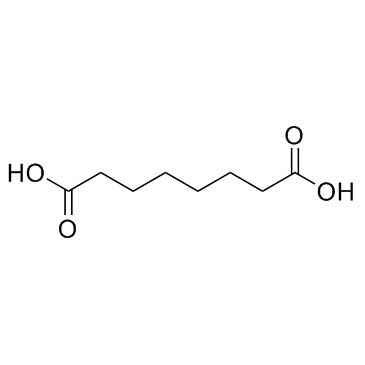
Octanedioic acid structure
|
Common Name | Octanedioic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 505-48-6 | Molecular Weight | 174.194 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 361.2±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H14O4 | Melting Point | 140-144 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 186.5±19.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Octanedioic acidOctanedioic acid is found to be associated with carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency, malonyl-Coa decarboxylase deficiency. |
| Name | suberic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Octanedioic acid is found to be associated with carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency, malonyl-Coa decarboxylase deficiency. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 361.2±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 140-144 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H14O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 174.194 |
| Flash Point | 186.5±19.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 174.089203 |
| PSA | 74.60000 |
| LogP | 0.80 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.476 |
| InChIKey | TYFQFVWCELRYAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CCCCCCC(=O)O |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, reducing agents, bases. |
| Water Solubility | 0.6 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| HS Code | 2917190090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2917190090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2917190090 acyclic polycarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Physiology and pathophysiology of organic acids in cerebrospinal fluid.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 16(4) , 648-69, (1993) Concentrations of organic acids in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) appear to be directly dependent upon their rate of production in the brain. There is evidence that the net release of short-chain monocarbo... |
|
|
Age-related reference values for urinary organic acids in a healthy Turkish pediatric population.
Clin. Chem. 40(6) , 862-6, (1994) Organic acid concentrations were quantified by gas chromatography and the individual acids identified by mass spectrometry in urine specimens from a healthy Turkish pediatric population of ages 2 days... |
|
|
Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression.
Nature 457(7231) , 910-4, (2009) Multiple, complex molecular events characterize cancer development and progression. Deciphering the molecular networks that distinguish organ-confined disease from metastatic disease may lead to the i... |
| octanedinoic acid diethyl ester |
| EINECS 208-010-9 |
| Suberic acid |
| MFCD00004428 |
| Octandisaeure-diaethylester |
| Ethyl suberate |
| SUBERIC ACID DIETHYL ESTER |
| 1,8-diethyl octanedioate |
| DIETHYL SUBERATE |
| Korksaeurediaethylester |
| Octanedioic acid |
| 1,6-hexanedicarboxylic acid |
| octanedioic acid diethyl ester |
 CAS#:502-49-8
CAS#:502-49-8 CAS#:931-88-4
CAS#:931-88-4 CAS#:65111-06-0
CAS#:65111-06-0 CAS#:629-40-3
CAS#:629-40-3 CAS#:27607-33-6
CAS#:27607-33-6 CAS#:42565-22-0
CAS#:42565-22-0 CAS#:696-71-9
CAS#:696-71-9 CAS#:5698-50-0
CAS#:5698-50-0 CAS#:292-64-8
CAS#:292-64-8 CAS#:10521-06-9
CAS#:10521-06-9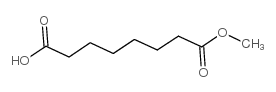 CAS#:3946-32-5
CAS#:3946-32-5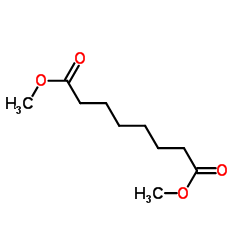 CAS#:1732-09-8
CAS#:1732-09-8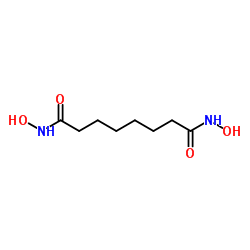 CAS#:38937-66-5
CAS#:38937-66-5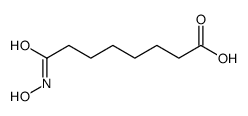 CAS#:149647-86-9
CAS#:149647-86-9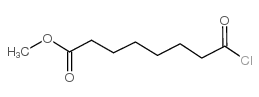 CAS#:41624-92-4
CAS#:41624-92-4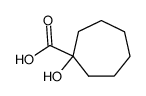 CAS#:20920-03-0
CAS#:20920-03-0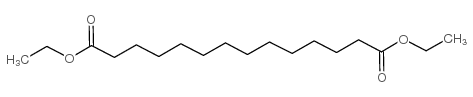 CAS#:19812-63-6
CAS#:19812-63-6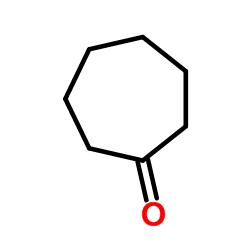 CAS#:502-42-1
CAS#:502-42-1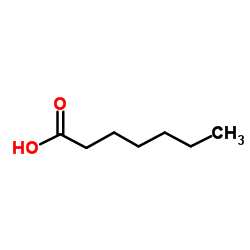 CAS#:111-14-8
CAS#:111-14-8
