Isotretinoin
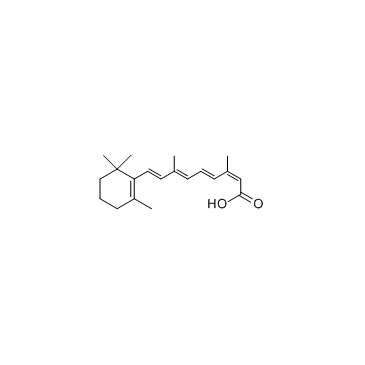
Isotretinoin structure
|
Common Name | Isotretinoin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4759-48-2 | Molecular Weight | 300.435 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 462.8±14.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H28O2 | Melting Point | 172-175 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 350.6±11.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of IsotretinoinIsotretinoin(13-cis-Retinoic acid) is a medication used for the treatment of severe acne. It was first developed to be used as a chemotherapy medication for the treatment of brain cancer, pancreatic cancer and more.Target: RAR/RXRIsotretinoin has been the most effective and long-lasting drug for the treatment of severe acne for more than 30 years and can achieve long-term remission in 70-80% of patients after a single course. The new evidence-based European S3-guideline recommends the use of Isotretinoin as a first-line medication for the treatment of severe papulopustular or conglobate acne, especially when prognostically unfavorable factors are present: family history of acne, early onset, marked seborrhea, localization on the trunk, scarring, psychosocial disability or persistent/late-type acne [1]. Five patients with pityriasis rubra pilaris were treated with isotretinoin from September 1982 through 1985. Isotretinoin at an average dose of 1.16 mg/kg/day for 16 to 24 weeks caused complete or almost complete clearing in four of the five patients [2]. isotretinoin produces significant anti-inflammatory effects by inhibition of monocyte and neutrophil chemotaxis across intact biologic barriers in vivo [3]. Isotretinoin 5 mg/day is effective in reducing the number of acne lesions, and improving patients dermatologic quality of life, with minimal adverse effects [4]. Clinical indications: Acne Toxicity: Isotretinoin is teratogenic. It also causes mucocutaneous side effects suck as cheilitis, dry skin, and dry eyes. |
| Name | isotretinoin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Isotretinoin(13-cis-Retinoic acid) is a medication used for the treatment of severe acne. It was first developed to be used as a chemotherapy medication for the treatment of brain cancer, pancreatic cancer and more.Target: RAR/RXRIsotretinoin has been the most effective and long-lasting drug for the treatment of severe acne for more than 30 years and can achieve long-term remission in 70-80% of patients after a single course. The new evidence-based European S3-guideline recommends the use of Isotretinoin as a first-line medication for the treatment of severe papulopustular or conglobate acne, especially when prognostically unfavorable factors are present: family history of acne, early onset, marked seborrhea, localization on the trunk, scarring, psychosocial disability or persistent/late-type acne [1]. Five patients with pityriasis rubra pilaris were treated with isotretinoin from September 1982 through 1985. Isotretinoin at an average dose of 1.16 mg/kg/day for 16 to 24 weeks caused complete or almost complete clearing in four of the five patients [2]. isotretinoin produces significant anti-inflammatory effects by inhibition of monocyte and neutrophil chemotaxis across intact biologic barriers in vivo [3]. Isotretinoin 5 mg/day is effective in reducing the number of acne lesions, and improving patients dermatologic quality of life, with minimal adverse effects [4]. Clinical indications: Acne Toxicity: Isotretinoin is teratogenic. It also causes mucocutaneous side effects suck as cheilitis, dry skin, and dry eyes. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 462.8±14.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 172-175 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C20H28O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 300.435 |
| Flash Point | 350.6±11.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 300.208923 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 6.83 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.556 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Stability | Stable, but probably air and light sensitive. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335-H360 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38;R61 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S26-S36/37/39-S45-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VH6440000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 5 | |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI typ... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals ... |
| EINECS 225-296-0 |
| sotret |
| isotrex |
| ROACCUTANE |
| Retinoin |
| MFCD00079542 |
| Claravis |
| Accutane |
| teriosal |
| (2Z,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid |
| Isoretinoin |
| Ro 4-3780 |
| Retinoic acid, 13-cis- |
| cis-retinoic acid |
| 13-cis-ra |
| (13Z)-Retinoic Acid |
| Retinoic acid 13-cis-form |
| (13cis)-Retinoic acid |
| 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2-cis-4-trans-6-trans-8-trans-nonatetraenoic acid |
| 13-cis-Retinoic acid |
| (2Z,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid |
| 13-ra |
| 13-cis-vitamin A acid |
| Isotretinoin |
| Retinoic acid, (13cis)- |
| Amnesteem |
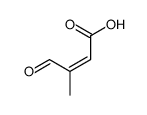 CAS#:70143-04-3
CAS#:70143-04-3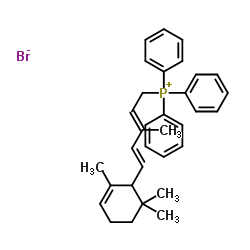 CAS#:62285-98-7
CAS#:62285-98-7 CAS#:302-79-4
CAS#:302-79-4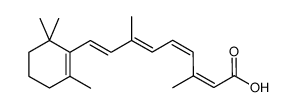 CAS#:3555-80-4
CAS#:3555-80-4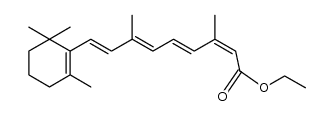 CAS#:59699-82-0
CAS#:59699-82-0![4-methyl-6-[(1E,3E)-2-methyl-4-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)buta-1,3-dien-1-yl]-5,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/277/43059-50-3.png) CAS#:43059-50-3
CAS#:43059-50-3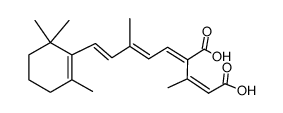 CAS#:81176-73-0
CAS#:81176-73-0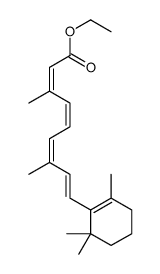 CAS#:3899-20-5
CAS#:3899-20-5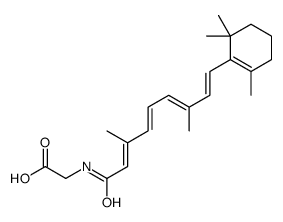 CAS#:110848-62-9
CAS#:110848-62-9 CAS#:16760-45-5
CAS#:16760-45-5 CAS#:75686-04-3
CAS#:75686-04-3 CAS#:75686-07-6
CAS#:75686-07-6 CAS#:84680-31-9
CAS#:84680-31-9
