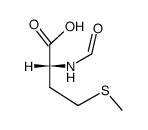
Formyl-L-methionine
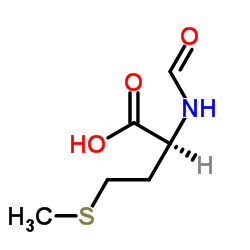
Formyl-L-methionine structure
|
Common Name | Formyl-L-methionine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4289-98-9 | Molecular Weight | 177.221 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 453.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H11NO3S | Melting Point | 101 ℃ | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 228.1±27.3 °C | |
Use of Formyl-L-methionineN-Formylmethionine is effective in the initiation of protein synthesis. The initiating methionine residue enters the ribosome as N-formylmethionyl tRNA. This process occurs in Escherichia coli and other bacteria as well as in the mitochondria of eucaryotic cells. |
| Name | N-formyl-L-methionine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 453.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 101 ℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C6H11NO3S |
| Molecular Weight | 177.221 |
| Flash Point | 228.1±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 177.045959 |
| PSA | 91.70000 |
| LogP | 0.44 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.517 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|
~% 
Formyl-L-methionine CAS#:4289-98-9 |
| Literature: Windus; Marvel Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1931 , vol. 53, p. 3493 |
|
~% 
Formyl-L-methionine CAS#:4289-98-9 |
| Literature: Windus; Marvel Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1931 , vol. 53, p. 3493 |
|
~% 
Formyl-L-methionine CAS#:4289-98-9 |
| Literature: Muramatsu,I. et al. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 1965 , vol. 38, p. 244 - 246 |
|
~% 
Formyl-L-methionine CAS#:4289-98-9 |
| Literature: Windus; Marvel Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1931 , vol. 53, p. 3490 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
A novel amino acid analysis method using derivatization of multiple functional groups followed by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.
Analyst 140(6) , 1965-73, (2015) We have developed a novel amino acid analysis method using derivatization of multiple functional groups (amino, carboxyl, and phenolic hydroxyl groups). The amino, carboxyl, and phenolic hydroxyl grou... |
|
|
Functional roles of TAP and tapasin in the assembly of M3-N-formylated peptide complexes.
J. Immunol. 167(3) , 1507-14, (2001) H2-M3 is a MHC class Ib molecule with a high propensity to bind N-formylated peptides. Due to the paucity of endogenous Ag, the majority of M3 is retained in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Upon addit... |
|
|
Immunization with f-Met peptides induces immune reactivity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Tuber. Lung Dis. 80(1) , 5-13, (2000) Objective: To determine whether synthetic peptides containing an amino terminal formyl-methionine residue and corresponding to the sequence of several proteins produced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, ... |
| Formyl-L-methionine |
| 2-formamido-4-methylsulfanylbutanoic acid |
| (E)-N-(Hydroxymethylene)-L-methionine |
| (S)-2-Formamido-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid |
| N-Formyl-L -Methionine |
| L-Methionine, N-formyl- |
| N-Formyl-L-methionine |
| MFCD00021033 |
| DL-Methionine, N-formyl- |
| L-Methionine, N-(hydroxymethylene)-, (E)- |


 CAS#:63472-90-2
CAS#:63472-90-2
