Z-Guggulsterone
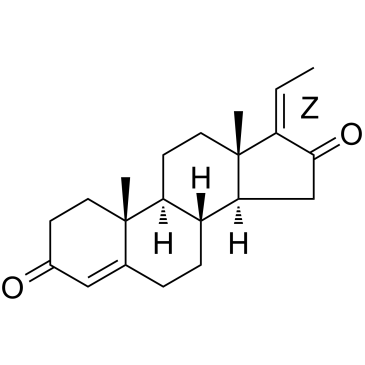
Z-Guggulsterone structure
|
Common Name | Z-Guggulsterone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 39025-23-5 | Molecular Weight | 312.446 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 463.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H28O2 | Melting Point | 188-190° | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 172.3±25.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Z-GuggulsteroneZ-guggulsterone, a constituent of Indian Ayurvedic medicinal plant Commiphora mukul, inhibits the growth of human prostate cancer cells by causing apoptosis. Z-guggulsterone inhibits angiogenesis by suppressing the VEGF–VEGF-R2–Akt signaling axis[1]. |
| Name | (Z)-Guggulsterone |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Z-guggulsterone, a constituent of Indian Ayurvedic medicinal plant Commiphora mukul, inhibits the growth of human prostate cancer cells by causing apoptosis. Z-guggulsterone inhibits angiogenesis by suppressing the VEGF–VEGF-R2–Akt signaling axis[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
VEGF-R2 Akt |
| In Vitro | Z-guggulsterone (10, 20 μM; 24 or 48 hours) causes a decrease in the level of VEGF-R2 protein in HUVEC[1]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) Concentration: 10, 20 μM Incubation Time: 24 or 48 hours Result: Caused a decrease in the level of VEGF-R2 protein in HUVEC. |
| In Vivo | Z-guggulsterone (oral; 1 mg; 5 times/week) results in a statistically significantly decrease in tumor volume and wet tumor weight[1]. Animal Model: Male nude mice (5–6 weeks old) s.c. implanted with DU145 cell-containing Matrigel plugs Dosage: 1 mg Administration: Oral; 5 times/week Result: Resulted in a statistically significantly decrease in tumor volume and wet tumor weight. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 463.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 188-190° |
| Molecular Formula | C21H28O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 312.446 |
| Flash Point | 172.3±25.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 312.208923 |
| PSA | 34.14000 |
| LogP | 3.65 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.557 |
| InChIKey | WDXRGPWQVHZTQJ-OSJVMJFVSA-N |
| SMILES | CC=C1C(=O)CC2C3CCC4=CC(=O)CCC4(C)C3CCC12C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain canc... |
|
|
Genetic mapping of targets mediating differential chemical phenotypes in Plasmodium falciparum.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 765-71, (2009) Studies of gene function and molecular mechanisms in Plasmodium falciparum are hampered by difficulties in characterizing and measuring phenotypic differences between individual parasites. We screened... |
|
|
Conformational dynamics of human FXR-LBD ligand interactions studied by hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass spectrometry: insights into the antagonism of the hypolipidemic agent Z-guggulsterone.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1844(9) , 1684-93, (2014) Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily of transcription factors that plays a key role in the regulation of bile acids, lipid and glucose metabolisms. The regulative... |
| Guggulsterone |
| (17E)-Pregna-4,17-diene-3,16-dione |
| (17Z)-Pregna-4,17(20)-diene-3,16-dione 4,17(20)-trans-Pregnadiene-3,16-dione |
| UNII:9B259YE66O |
| Pregna-4,17(20)-diene-3,16-dione, (17E)- |
| (17E)-Pregna-4,17(20)-diene-3,16-dione |
| Z-Guggulsterone,(Z)-Pregna-4,17(20)-diene-3,16-dione |
| E-guggulsterone |
| Pregna-4,17-diene-3,16-dione, (17E)- |
| trans-Guggulsterone |
| GUGGULSTERONE, (E)- |
 CAS#:3347-58-8
CAS#:3347-58-8