H-Gly-Ala-OH
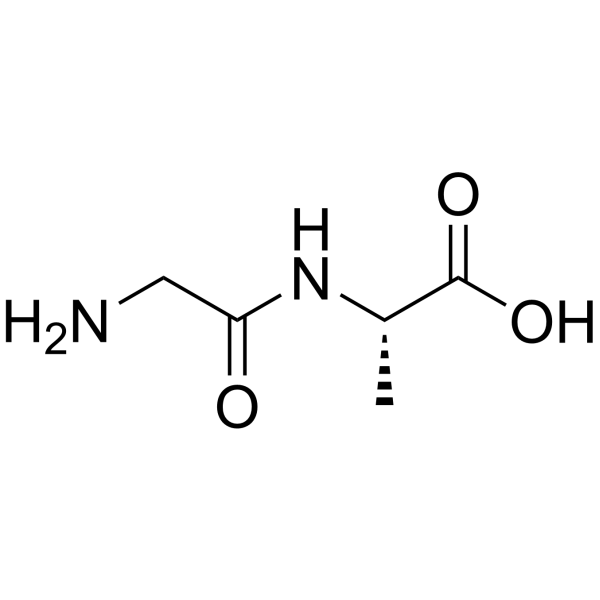
H-Gly-Ala-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-Gly-Ala-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3695-73-6 | Molecular Weight | 146.145 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 417.4±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10N2O3 | Melting Point | ~ 230°C dec. | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 206.2±24.6 °C | |
Use of H-Gly-Ala-OHGly-Ala is a Glycine (HY-Y0966) derivative[1]. |
| Name | Glycine-alanine dipeptide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Gly-Ala is a Glycine (HY-Y0966) derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 417.4±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | ~ 230°C dec. |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 146.145 |
| Flash Point | 206.2±24.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 146.069138 |
| PSA | 92.42000 |
| LogP | -1.50 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.498 |
| Storage condition | -15°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 6 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Charge-based interactions between peptides observed as the dominant force for association in aqueous solution.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 47(47) , 9059-62, (2008)
|
|
|
Epstein-Barr virus latent genes.
Exp. Mol. Med. 47 , e131, (2015) Latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection has a substantial role in causing many human disorders. The persistence of these viral genomes in all malignant cells, yet with the expression of limited late... |
|
|
Dissociative electron attachment to glycyl-glycine, glycyl-alanine and alanyl-alanine.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13(10) , 4600-6, (2011) The processes of negative ions formation of dipeptides glycyl-glycine, glycyl-alanine and alanyl-alanine in the conditions of resonant electron capture have been studied with a help of negative ions m... |
| EINECS 223-019-8 |
| Gly-l-ala |
| Glycyl-DL-alanine |
| Glycine-alanine |
| Glycyl-L-alanine |
| Gly-Ala-OH |
| MFCD00065112 |
| Glcylalanine |
| H-Gly-L-Ala-OH |
| UNII:44L9158R9G |
| N-glycylalanine |
| Gly-L-Ala-OH |
| Alanine, N-glycyl-, L- |
| L-Alanine, glycyl- |
| (S)-2-(2-Aminoacetamido)propanoic acid |
| Alanine, glycyl- |
| Glycylalanine |
| DL-Alanine, N-glycyl- |
| Gly-Ala |
| L-Alanine, N-glycyl- |
| N-Glycyl-L-alanine |
| H-GLY-ALA-OH |
| H-Gly-β-Ala-OH |
 CAS#:3079-63-8
CAS#:3079-63-8 CAS#:41445-61-8
CAS#:41445-61-8 CAS#:4066-24-4
CAS#:4066-24-4 CAS#:52162-82-0
CAS#:52162-82-0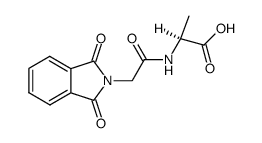 CAS#:5652-29-9
CAS#:5652-29-9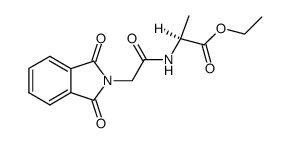 CAS#:70019-92-0
CAS#:70019-92-0 CAS#:4526-77-6
CAS#:4526-77-6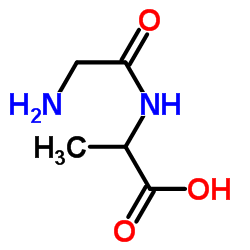 CAS#:926-77-2
CAS#:926-77-2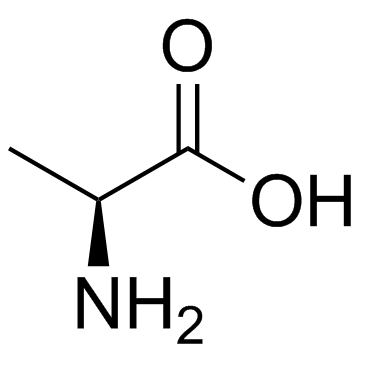 CAS#:56-41-7
CAS#:56-41-7 CAS#:56-40-6
CAS#:56-40-6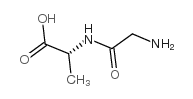 CAS#:691-81-6
CAS#:691-81-6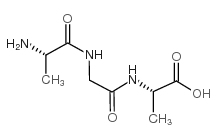 CAS#:37460-22-3
CAS#:37460-22-3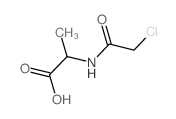 CAS#:691-80-5
CAS#:691-80-5
