Meranzin
Modify Date: 2025-08-31 17:34:18
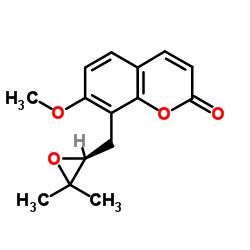
Meranzin structure
|
Common Name | Meranzin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 23971-42-8 | Molecular Weight | 260.285 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 414.8±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H16O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 185.3±28.8 °C | |
Use of MeranzinMeranzin is an absorbed bioactive compound from the Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Chaihu-Shugan-San (CSS). Meranzin, isolated from leaves of Murraya exotica L., regulates the shared alpha 2-adrenoceptor and involves the AMPA-ERK1/2–BDNF signaling pathway. Meranzin has the potential for the prevention of the comorbidity of atherosclerosis and depression[1][2]. |
| Name | 8-{[(2S)-3,3-Dimethyl-2-oxiranyl]methyl}-7-methoxy-2H-chromen-2-o ne |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Meranzin is an absorbed bioactive compound from the Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Chaihu-Shugan-San (CSS). Meranzin, isolated from leaves of Murraya exotica L., regulates the shared alpha 2-adrenoceptor and involves the AMPA-ERK1/2–BDNF signaling pathway. Meranzin has the potential for the prevention of the comorbidity of atherosclerosis and depression[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 414.8±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C15H16O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 260.285 |
| Flash Point | 185.3±28.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 260.104858 |
| PSA | 51.97000 |
| LogP | 1.92 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.567 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| pimelic acid monomethyl ester |
| 8-{[(2S)-3,3-Dimethyl-2-oxiranyl]methyl}-7-methoxy-2H-chromen-2-one |
| 6-methoxycarbonylhexanoic acid |
| methyl hydrogenpimelate |
| monomethyl heptanedioate |
| Heptanedioic acid,1-methyl ester |
| 2H-1-Benzopyran-2-one, 8-[[(2S)-3,3-dimethyloxiranyl]methyl]-7-methoxy- |
| Heptanedioic acid,monomethyl ester |
| Methyl hydrogen heptane-1,7-dioate |
| Monomethyl pimelate |

