BMS 493
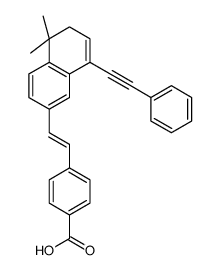
BMS 493 structure
|
Common Name | BMS 493 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 215030-90-3 | Molecular Weight | 404.50000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H24O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of BMS 493BMS493 is an inverse pan-retinoic acid receptor (RAR) agonist. BMS493 increases nuclear corepressor interaction with RARs. BMS493 also could prevent retinoic acid-induced differentiation[1][2]. |
| Name | 4-{(E)-2-[5,5-Dimethyl-8-(phenylethynyl)-5,6-dihydro-2-naphthalen yl]vinyl}benzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | BMS493 is an inverse pan-retinoic acid receptor (RAR) agonist. BMS493 increases nuclear corepressor interaction with RARs. BMS493 also could prevent retinoic acid-induced differentiation[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
RAR |
| In Vitro | BMS493 (100 nM; 6 days; ALDHhi UCB cells) treatment shows a twofold increase in the number of ALDHhi cells available for transplantation compared with untreated controls. Newly expanded ALDHhi cells shows increased numbers of CD34 and CD133-positive cells, as well as a reduction in CD38 expression, a marker of hematopoietic cell differentiation[1]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: ALDHhi UCB cells Concentration: 100 nM Incubation Time: 6 days Result: Showed a twofold increase in the number of ALDHhi cells available for transplantation compared with untreated controls. |
| In Vivo | Intrapancreatic transplantation of cell progeny after expansion of ALDHhi cells with or without BMS493 shows no reduction of hyperglycemia in Streptozotocin-treated NOD/SCID mice. Thus, Umbilical cord blood (UCB)-derived ALDHhi cells effectively lost islet regenerative capacity during ex vivo expansion[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C29H24O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 404.50000 |
| Exact Mass | 404.17800 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 6.67160 |
| Hazard Statements | H413 |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Trichostatin A reduces GnRH mRNA expression with a concomitant increase in retinaldehyde dehydrogenase in GnRH-producing neurons.
Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 413 , 113-9, (2015) Trichostatin A (TSA) is a selective inhibitor of mammalian histone deacetylase and is widely used to modify the ability of DNA transcription factors to bind DNA within chromatin by interfering with hi... |
|
|
Retinoic acid signalling regulates the development of tonotopically patterned hair cells in the chicken cochlea.
Nat. Commun. 5 , 3840, (2014) Precise frequency discrimination is a hallmark of auditory function in birds and mammals and is required for distinguishing similar sounding words, like 'bat,' 'cat' and 'hat.' In the cochlea, tuning ... |
|
|
Retinoic acid receptor alpha is associated with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer.
Nat. Commun. 4 , 2175, (2013) About one-third of oestrogen receptor alpha-positive breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen relapse. Here we identify the nuclear receptor retinoic acid receptor alpha as a marker of tamoxifen ... |
| 4-[(E)-(5 6-Dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-8-phenylethynyl-2-naphthalenyl)ethenyl]benzoic acid |
| (E)-4-[2-[2-[[(p-methoxyphenyl)sulfonyl]amino]phenyl]ethenyl]pyridine |
| (E)-4-(2-(2-(N-(4-METHOXYBENZENESULFONYL)AMINO)PHENYL)VINYL)PYRIDINE |
| (E)-4-[2-[5,6-dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-8-(2-phenylethynyl)naphthalen-2-yl]ethen-1-yl]benzoic acid |
| Benzenesulfonamide,4-methoxy-N-[2-[2-(4-pyridinyl)ethenyl]phenyl]-,(E) |
| (E)-4-[2-[5,6-dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-8-(2-phenylethynyl)naphthalene-2-yl]ethen-1-yl]benzoic acid |
| Benzenesulfonamide,4-methoxy-N-[2-[(1E)-2-(4-pyridinyl)ethenyl]phenyl] |
| (E)-4-[2-{2-[N-(4-methoxybenzenesulfonyl)amino]phenyl}ethenyl ]pyridine |
| (E)-4-[2-[2-[N-[(p-Methoxyphenyl)sulfonyl]amino]phenyl]ethenyl]pyridine |
| (E)-4-[2-[2-(p-methoxy-benzene-sulfonamide)phenyl]ethenyl]pyridine |
| BMS-204493 |