L-Inosine
Modify Date: 2025-08-24 13:34:11
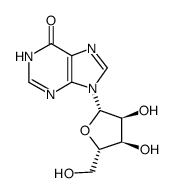
L-Inosine structure
|
Common Name | L-Inosine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 21138-24-9 | Molecular Weight | 268.22600 | |
| Density | 2.08 | Boiling Point | 732.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12N4O5 | Melting Point | 218ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of L-InosineL-Inosine is the L-configuration of Inosine (HY-N0092). Inosine is an endogenous purine nucleoside produced by catabolism of adenosine. Inosine has anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive, immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effects[1][2]. |
| Name | L-Inosine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Inosine is the L-configuration of Inosine (HY-N0092). Inosine is an endogenous purine nucleoside produced by catabolism of adenosine. Inosine has anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive, immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effects[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 2.08 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 732.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 218ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12N4O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 268.22600 |
| Exact Mass | 268.08100 |
| PSA | 133.49000 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| 9-pentofuranosyl-1,9-dihydro-purin-6-one |
| 9-oxy-9-isopropyl-fluorene |
 CAS#:58-61-7
CAS#:58-61-7