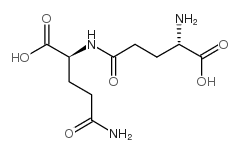
L-GlutaMic acid γ-MonohydroxaMate
L-GlutaMic acid γ-MonohydroxaMate structure
|
Common Name | L-GlutaMic acid γ-MonohydroxaMate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1955-67-5 | Molecular Weight | 162.14400 | |
| Density | 1.432g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 553.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10N2O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 288.6ºC | |
Use of L-GlutaMic acid γ-MonohydroxaMateL-Glutamic γ-monohydroxamate is an antitumor agent, inhibits cell proliferation. L-Glutamic γ-monohydroxamate selectively inhibits the uptake of L-histidine into microvascular endothelial cell. L-Glutamic γ-monohydroxamate, as a vanadium ligand, activates glucose uptake and metabolism, thus decreases the blood glucose levels in vivo[1][2][3]. |
| Name | glutamine hydroxamate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Glutamic γ-monohydroxamate is an antitumor agent, inhibits cell proliferation. L-Glutamic γ-monohydroxamate selectively inhibits the uptake of L-histidine into microvascular endothelial cell. L-Glutamic γ-monohydroxamate, as a vanadium ligand, activates glucose uptake and metabolism, thus decreases the blood glucose levels in vivo[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.432g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 553.6ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 162.14400 |
| Flash Point | 288.6ºC |
| Exact Mass | 162.06400 |
| PSA | 116.14000 |
| LogP | 0.22450 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.46E-14mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.538 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2928000090 |
| HS Code | 2928000090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2928000090 other organic derivatives of hydrazine or of hydroxylamine VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:20.0% |
|
Cell differentiation of Proteus mirabilis is initiated by glutamine, a specific chemoattractant for swarming cells.
Mol. Microbiol. 8(1) , 53-60, (1993) Swarming by Proteus mirabilis involves differentiation of typical short vegetative rods into filamentous hyperflagellated swarm cells which undergo cycles of rapid and co-ordinated population migratio... |
|
|
Alternative substrates for wild-type and L109A E. coli CTP synthases: kinetic evidence for a constricted ammonia tunnel.
Eur. J. Biochem. 271(21) , 4204-12, (2004) Cytidine 5'-triphosphate (CTP) synthase catalyses the ATP-dependent formation of CTP from uridine 5'-triphosphate using either NH(3) or l-glutamine as the nitrogen source. The hydrolysis of glutamine ... |
|
|
Effect of epidermal growth factor on glutamine metabolic enzymes in small intestine and skeletal muscle of parenterally fed rats.
Nutrition 13(7-8) , 652-5, (1997) Exogenous epidermal growth factor (EGF) markedly increases the in vivo uptake of glutamine by small intestine during total parenteral nutrition (TPN). Since glutamine is the major oxidative fuel for t... |
| (4S)-4-Amino-4-carboxybutanehydroxamic acid |
| (2S)-5-amino-2-(hydroxyamino)-5-keto-valeric acid |
| N5-Hydroxy-L-glutamine |
| (S)-4-Amino-4-carboxybutanehydroximic acid |
| 3-[2-Oxo-2-(hydroxyamino)ethyl]alanine |
| (2S)-2-Amino-5-oxo-5-(hydroxyamino)pentanoic acid |
| AMINO ACID HYDROXAMATES L-GLUTAMIC ACID γ-MONOHYDROXAMATE |
| L-GlutaMic acid γ-MonohydroxaMate |