TPMPA
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 15:03:31
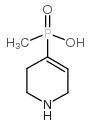
TPMPA structure
|
Common Name | TPMPA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 182485-36-5 | Molecular Weight | 161.13900 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12NO2P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of TPMPATPMPA, a hybrid of isoguvacine and 3-APMPA, is the first selective antagonist for a GABAC receptor (KB = 2.1 μM), but not to interact with GABAA (KB = 320 μM) or GABAB receptors (EC50 = 500 μM). TPMPA has the potential for the research of suppressing orientation selectivity in ganglion cells[1][2][3]. |
| Name | (1,2,5,6-Tetrahydropyridin-4-yl)methylphosphinic acid hydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | TPMPA, a hybrid of isoguvacine and 3-APMPA, is the first selective antagonist for a GABAC receptor (KB = 2.1 μM), but not to interact with GABAA (KB = 320 μM) or GABAB receptors (EC50 = 500 μM). TPMPA has the potential for the research of suppressing orientation selectivity in ganglion cells[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
KB: 2.1 μM (GABAC) |
| In Vitro | TPMPA antagonizes the GABA currents of ρ1 receptors (IC50 = 1.6 μM) and those of the chimeric ρ1/α1 receptors with approximately the same potency (IC50 = 1.3 μM)[1]. TPMPA shows weak activity against rho-1 and rho-2 receptors, with the KB values of 2.0 and 15.6 μM, respectively[2] |
| References |
[2]. Graham A. R. Johnston, et al. Neurologically-active compounds. WO1998058939A1 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12NO2P |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 161.13900 |
| Exact Mass | 161.06100 |
| PSA | 59.14000 |
| LogP | 1.09260 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|---|
| (1,2,5,6-Tetrahydropyridin-4-yl)methylphosphinicacid |
| TPMPA hydrate |
| TPMPA |