Magnesium acetate tetrahydrate
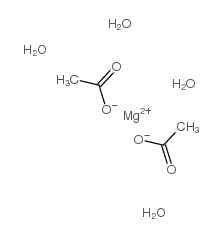
Magnesium acetate tetrahydrate structure
|
Common Name | Magnesium acetate tetrahydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 16674-78-5 | Molecular Weight | 214.45400 | |
| Density | 1.454 | Boiling Point | 117.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H14MgO8 | Melting Point | 72-75 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Magnesium acetate tetrahydrateMagnesium acetate tetrahydrate is a hydrated form of anhydrous magnesium acetate salt. As a salt form of Magnesium, Magnesium acetate is one of the bioavailable forms of magnesium and forms a very water soluble compound. Magnesium acetate tetrahydrate can be used as an electrolyte supplementation or a reagent in molecular biology experiments[1]. |
| Name | Magnesium acetate tetrahydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Magnesium acetate tetrahydrate is a hydrated form of anhydrous magnesium acetate salt. As a salt form of Magnesium, Magnesium acetate is one of the bioavailable forms of magnesium and forms a very water soluble compound. Magnesium acetate tetrahydrate can be used as an electrolyte supplementation or a reagent in molecular biology experiments[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Microbial Metabolite Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.454 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 117.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 72-75 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H14MgO8 |
| Molecular Weight | 214.45400 |
| Exact Mass | 214.05400 |
| PSA | 117.18000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 13.9mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | n20/D 1.358 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | 1200 g/L (15 ºC) |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AI5600000 |
| HS Code | 29152900 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |
| HS Code | 29152900 |
|---|
|
Cell-free expression and in meso crystallisation of an integral membrane kinase for structure determination.
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 71(24) , 4895-910, (2014) Membrane proteins are key elements in cell physiology and drug targeting, but getting a high-resolution structure by crystallographic means is still enormously challenging. Novel strategies are in big... |
|
|
A class III chitinase without disulfide bonds from the fern, Pteris ryukyuensis: crystal structure and ligand-binding studies.
Planta 242 , 895-907, (2015) We first solved the crystal structure of class III catalytic domain of a chitinase from fern (PrChiA-cat), and found a structural difference between PrChiA-cat and hevamine. PrChiA-cat was found to ha... |
|
|
Coat Protein-Dependent Behavior of Poly(ethylene glycol) Tails in Iron Oxide Core Virus-like Nanoparticles.
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7 , 12089-98, (2015) Here we explore the formation of virus-like nanoparticles (VNPs) utilizing 22-24 nm iron oxide nanoparticles (NPs) as cores and proteins derived from viral capsids of brome mosaic virus (BMV) or hepat... |
| magnesium,diacetate,tetrahydrate |
| EINECS 205-554-9 |
| Magnesium acetate tetrahydrate |
| MFCD00149214 |
 CAS#:3006-93-7
CAS#:3006-93-7 CAS#:142-72-3
CAS#:142-72-3 CAS#:7732-18-5
CAS#:7732-18-5 CAS#:3581-93-9
CAS#:3581-93-9
