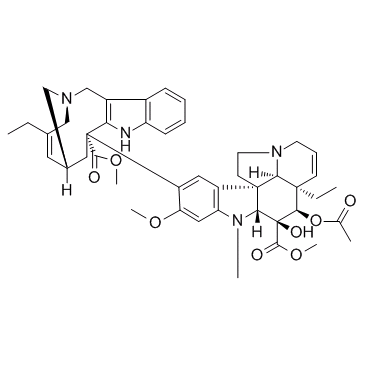
Vinflunine
Modify Date: 2025-08-20 21:45:04
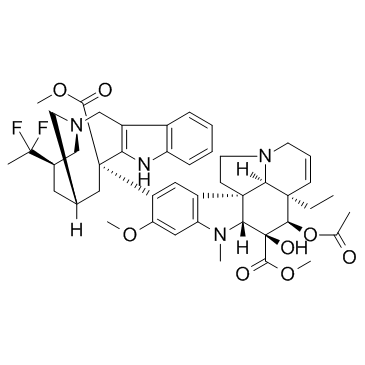
Vinflunine structure
|
Common Name | Vinflunine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 162652-95-1 | Molecular Weight | 816.92900 | |
| Density | 1.39 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C45H54F2N4O8 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of VinflunineVinflunine is a new vinca alkaloid uniquely fluorinated with the properties of mitotic-arresting and tubulin-interacting activity.Target: Microtubule/TubulinThe major effects of Vinflunine on dynamic instability are a slowing of the microtubule growth rate, an increase in growth duration, and a reduction in shortening duration. The effects of Vinflunine on the readmilling rate is examined by following [3H]GTP incorporation into MAP-rich microtubules, and the IC50 is 0.42 μM [1]. Vinflunine induced mitotic accumulation with IC50 with 18.8 nM, which decreases the centromere dynamicity by 44% and increases the time centromeres spent ina paused state by 63% [2]. Treatment of Vinflunine induces a rapid change in endothelial cell shape: cells retracts and assumes a rounded morphology. Mean IC50 values are 9.9 × 10-5 M × 10-5 M for fibronectin and 5.0× 10-5 M × 10-5 M for type IV collagen. A short 4 hours exposure of endothelial cells to Vinflunine at 10-8 0.05). An ID50 value (dose which inhibits 50% of bFGF-induced neovascularisation) is calculated as 1 mg/kg. Low doses of Vinflunine reduce the number of experimental liver metastases by human LS174T colon cancer cell. A slight overall decrease in liver metastatic foci is already observed at the very low dose of 0.16 mg/kg Vinflunine, although maximal overall inhibition is reached at the maximal tolerated dose (MTD) of 20 mg/kg [3]. |
| Name | Vinflunine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Vinflunine is a new vinca alkaloid uniquely fluorinated with the properties of mitotic-arresting and tubulin-interacting activity.Target: Microtubule/TubulinThe major effects of Vinflunine on dynamic instability are a slowing of the microtubule growth rate, an increase in growth duration, and a reduction in shortening duration. The effects of Vinflunine on the readmilling rate is examined by following [3H]GTP incorporation into MAP-rich microtubules, and the IC50 is 0.42 μM [1]. Vinflunine induced mitotic accumulation with IC50 with 18.8 nM, which decreases the centromere dynamicity by 44% and increases the time centromeres spent ina paused state by 63% [2]. Treatment of Vinflunine induces a rapid change in endothelial cell shape: cells retracts and assumes a rounded morphology. Mean IC50 values are 9.9 × 10-5 M × 10-5 M for fibronectin and 5.0× 10-5 M × 10-5 M for type IV collagen. A short 4 hours exposure of endothelial cells to Vinflunine at 10-8 0.05). An ID50 value (dose which inhibits 50% of bFGF-induced neovascularisation) is calculated as 1 mg/kg. Low doses of Vinflunine reduce the number of experimental liver metastases by human LS174T colon cancer cell. A slight overall decrease in liver metastatic foci is already observed at the very low dose of 0.16 mg/kg Vinflunine, although maximal overall inhibition is reached at the maximal tolerated dose (MTD) of 20 mg/kg [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.39 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C45H54F2N4O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 816.92900 |
| Exact Mass | 816.39100 |
| PSA | 133.87000 |
| LogP | 5.01950 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.652 |
| InChIKey | NMDYYWFGPIMTKO-ACNJXBQRSA-N |
| SMILES | CCC12C=CCN3CCC4(c5cc(C6(C(=O)OC)CC7CC(C(C)(F)F)CN(Cc8c6[nH]c6ccccc86)C7)c(OC)cc5N(C)C4C(O)(C(=O)OC)C1OC(C)=O)C32 |
|
~34% 
Vinflunine CAS#:162652-95-1 |
| Literature: Fahy; Duflos; Ribet; Jacquesy; Berrier; Jouannetaud; Zunino Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1997 , vol. 119, # 36 p. 8576 - 8577 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| 4'-Deoxy-20' |
| Methyl (2β,3β,4β,5α,12β,19α)-4-acetoxy-15-[(12S,14R,16R)-16-(1,1-difluoroethyl)-12-(methoxycarbonyl)-1,10-diazatetracyclo[12.3.1.0.0]octadeca-3(11),4,6,8-tetraen-12-yl]-
 3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-1-methyl-6,7-didehydroaspidospermidine-3-carboxylate |
| 4'-Deoxy-20',20'-difluoro-8'-norvincaleukoblastine |
| MFCD00938122 |
| C'-Norvincaleukoblastine,4'-deoxy-20',20'-difluoro |
| aspidospermidine-3-carboxylic acid, 4-(acetyloxy)-6,7-didehydro-15-[(4R,6R,8S)-4-(1,1-difluoroethyl)-1,3,4,5,6,7,8,9-octahydro-8-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,6-methano-2H-azecino[4,3-b]indol-8-yl]-3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-1-methyl-, methyl ester, (2β,3β,4β,5α,12β,19α)- |
| 20',20'-difluoro-3',4'-dihydrovinorelbine |
| Methyl (2β,3β,4β,5α,12β,19α)-4-acetoxy-15-[(12S,14R,16R)-16-(1,1-difluoroethyl)-12-(methoxycarbonyl)-1,10-diazatetracyclo[12.3.1.0.0]octadeca-3(11),4,6,8-tetraen-12-yl]-3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-1-methyl-6,7-didehydroaspidospermidine-3-carboxylate |
| C45H54F2N4O8 |
| Aspidospermidine-3-carboxylic acid, 4-(acetyloxy)-6,7-didehydro-15-[(4R,6R,8S)-4-(1,1-difluoroethyl)-1,3,4,5,6,7,8,9-octahydro-8-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,6-methano-2H-azecino[4,3-b]indol-8-yl]-3-hydroxy-16 ;-methoxy-1-methyl-, methyl ester, (2β,3β,4β,5α,12β,19α)- |
| methyl (2β,3β,4β,5α,12β,19α)-4-(acetyloxy)-15-[(4R,6R,8S)-4-(1,1-difluoroethyl)-8-(methoxycarbonyl)-1,3,4,5,6,7,8,9-octahydro-2,6-methanoazecino[4,3-b]indol-8-yl]-3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-1-methyl-6,7-didehydroaspidospermidine-3-carboxylate |