N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine

N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine structure
|
Common Name | N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 150-25-4 | Molecular Weight | 163.17 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 388.5±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO4 | Melting Point | 190 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 188.8±23.7 °C | |
Use of N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycineBicine is a useful buffer in the range of physiological interest. Bicine is a derivative of the simple amino acid glycine[1]. |
| Name | N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Bicine is a useful buffer in the range of physiological interest. Bicine is a derivative of the simple amino acid glycine[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 388.5±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 190 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 163.17 |
| Flash Point | 188.8±23.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 163.084457 |
| PSA | 81.00000 |
| LogP | -0.47 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.526 |
| InChIKey | FSVCELGFZIQNCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CN(CCO)CCO |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
| HS Code | 29225000 |
|---|
|
Endothelial transcriptome in response to pharmacological methyltransferase inhibition.
ChemMedChem 9(8) , 1755-62, (2014) The enzymatic activities of protein methyltransferases serve to write covalent modifications on histone and non-histone proteins in the control of gene transcription. Here, we describe gene expression... |
|
|
A Comprehensive Immunoreceptor Phosphotyrosine-based Signaling Network Revealed by Reciprocal Protein-Peptide Array Screening.
Mol. Cell. Proteomics 14 , 1846-58, (2015) Cells of the immune system communicate with their environment through immunoreceptors. These receptors often harbor intracellular tyrosine residues, which, when phosphorylated upon receptor activation... |
|
|
Solubilization of gliadins for use as a source of nitrogen in the selection of bacteria with gliadinase activity.
Food Chem. 168 , 439-44, (2014) For patients with celiac disease, gliadin detoxification via the use of gliadinases may provide an alternative to a gluten-free diet. A culture medium, in which gliadins were the sole source of nitrog... |
| Diethylolglycine |
| N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine,BICINE,PEG Grid Screening |
| Di(hydroxyethyl)glycine |
| Glycine, N, N-dihydroxyethyl- |
| N,N-Dihydroxyethyl glycine |
| bicine buffer |
| Bis(2-Hydroxyethyl)glycine |
| Bicine |
| BICINE[N,N-Di(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine] |
| EINECS 205-755-1 |
| Bicene |
| N,N-Bis(b-hydroxyethyl)glycine |
| N,N-Di(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine |
| Glycine, N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)- |
| Diethanolglycine |
| 2-[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]acetic acid |
| 2-HxG |
| 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)acetic acid |
| N,N-Bis(β-hydroxyethyl)glycine |
| MFCD00004295 |
| (Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)acetic Acid |
| Glycine, N,N-bis (2-hydroxyethyl)- |
| N,N-dihydroxyethylglycine |
| N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)aminoacetic acid |
| N,N-Bis(hydroxyethyl)glycine |
| N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine |
| N,N-Di(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine [Good's buffer component |
| N,N-Di(hydroxyethyl)aminoacetic Acid |
| Diethanol glycine |
| N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine (Bicine) |
| Dihydroxyethylglycine |
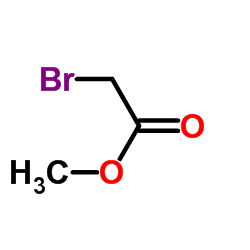 CAS#:96-32-2
CAS#:96-32-2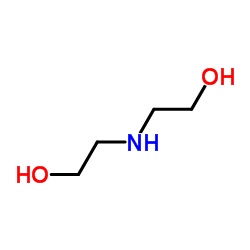 CAS#:111-42-2
CAS#:111-42-2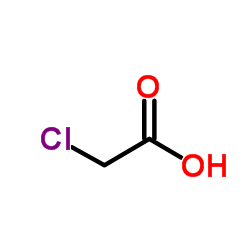 CAS#:79-11-8
CAS#:79-11-8![2-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]acetic acid Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/034/98486-41-0.png) CAS#:98486-41-0
CAS#:98486-41-0 CAS#:64-69-7
CAS#:64-69-7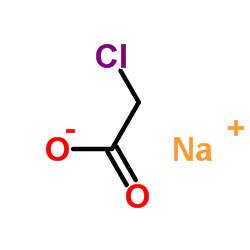 CAS#:3926-62-3
CAS#:3926-62-3 CAS#:50-00-0
CAS#:50-00-0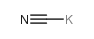 CAS#:151-50-8
CAS#:151-50-8![5-phenyl-4,6,11-trioxa-1-aza-5-silabicyclo[3.3.3]undecan-3-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/347/53883-47-9.png) CAS#:53883-47-9
CAS#:53883-47-9![5-methyl-4,6,11-trioxa-1-aza-5-silabicyclo[3.3.3]undecan-3-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/261/53883-49-1.png) CAS#:53883-49-1
CAS#:53883-49-1![5-ethenyl-4,6,11-trioxa-1-aza-5-silabicyclo[3.3.3]undecan-3-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/130/53883-57-1.png) CAS#:53883-57-1
CAS#:53883-57-1
