Domoic acid
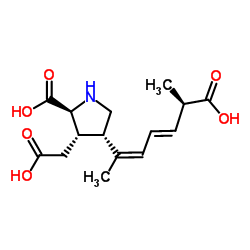
Domoic acid structure
|
Common Name | Domoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 14277-97-5 | Molecular Weight | 311.330 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 607.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H21NO6 | Melting Point | 228ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 321.0±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Domoic acidDomoic acid ((-)-Domoic acid; L-Domoic acid) is an excitatory neurotransmitter isolated from a form of marine vegetation, Nitzschia pungens[1]. Domoic acid produces neurotoxic effect through activating kainate receptor[2]. |
| Name | domoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Domoic acid ((-)-Domoic acid; L-Domoic acid) is an excitatory neurotransmitter isolated from a form of marine vegetation, Nitzschia pungens[1]. Domoic acid produces neurotoxic effect through activating kainate receptor[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 607.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 228ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C15H21NO6 |
| Molecular Weight | 311.330 |
| Flash Point | 321.0±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 311.136902 |
| PSA | 123.93000 |
| LogP | 0.61 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.545 |
| InChIKey | VZFRNCSOCOPNDB-AOKDLOFSSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=CC=CC(C)C(=O)O)C1CNC(C(=O)O)C1CC(=O)O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H332 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| RIDADR | UX9665100 |
| RTECS | UX9665100 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Metal-organic framework UiO-66 modified magnetite@silica core-shell magnetic microspheres for magnetic solid-phase extraction of domoic acid from shellfish samples.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1400 , 10-8, (2015) Fe3O4@SiO2@UiO-66 core-shell magnetic microspheres were synthesized and characterized by transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared s... |
|
|
The prostaglandin EP1 receptor potentiates kainate receptor activation via a protein kinase C pathway and exacerbates status epilepticus.
Neurobiol. Dis. 70 , 74-89, (2014) Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) regulates membrane excitability, synaptic transmission, plasticity, and neuronal survival. The consequences of PGE2 release following seizures has been the subject of much stud... |
|
|
Ursolic acid improves domoic acid-induced cognitive deficits in mice.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 271(2) , 127-36, (2013) Our previous findings suggest that mitochondrial dysfunction is the mechanism underlying cognitive deficits induced by domoic acid (DA). Ursolic acid (UA), a natural triterpenoid compound, possesses m... |
| (3S,4S)-4-[(2Z,4E,6R)-6-Carboxyhepta-2,4-dien-2-yl]-3-(carboxymethyl)-L-proline |
| L-Proline, 3-(carboxymethyl)-4-[(1Z,3E,5R)-5-carboxy-1-methyl-1,3-hexadien-1-yl]-, (3S,4S)- |
| Domoic acid,(2S,3S,4R,5'R)-2-Carboxy-4-(5'-carboxy-1'-methyl-1Z,3E-hexadienyl)-3-pyrrolidineaceticacid |
| [2S-[2a,3b,4b(1Z,3E,5S*)]]-2-Carboxy-4-(5-carboxy-1-methyl-1,3-hexadienyl)-3-pyrrolidineacetic Acid |
| Domoic acid |
| MFCD00040640 |
| L-Domoic acid |
| (3S,4S)-4-[(2Z,4E,6R)-6-Carboxy-2,4-heptadien-2-yl]-3-(carboxymethyl)-L-proline |
 CAS#:81658-31-3
CAS#:81658-31-3 CAS#:81658-33-5
CAS#:81658-33-5 CAS#:81658-34-6
CAS#:81658-34-6 CAS#:81658-32-4
CAS#:81658-32-4 CAS#:81658-35-7
CAS#:81658-35-7 CAS#:81658-36-8
CAS#:81658-36-8 CAS#:81658-29-9
CAS#:81658-29-9 CAS#:81658-41-5
CAS#:81658-41-5 CAS#:81703-63-1
CAS#:81703-63-1