5-Chloro-8-hydroxyquinoline
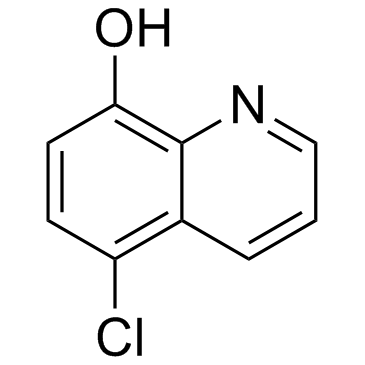
5-Chloro-8-hydroxyquinoline structure
|
Common Name | 5-Chloro-8-hydroxyquinoline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 130-16-5 | Molecular Weight | 179.603 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 348.7±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H6ClNO | Melting Point | 122-124 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 164.7±22.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 5-Chloro-8-hydroxyquinolineCloxiquine is an antibacterial, antifungal, antiaging and antituberculosis drug. |
| Name | 5-Chloro-8-hydroxyquinoline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cloxiquine is an antibacterial, antifungal, antiaging and antituberculosis drug. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 348.7±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 122-124 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H6ClNO |
| Molecular Weight | 179.603 |
| Flash Point | 164.7±22.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 179.013794 |
| PSA | 33.12000 |
| LogP | 3.02 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.697 |
| InChIKey | CTQMJYWDVABFRZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Oc1ccc(Cl)c2cccnc12 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VC4590000 |
| HS Code | 2933499090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933499090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933499090. other compounds containing in the structure a quinoline or isoquinoline ring-system (whether or not hydrogenated), not further fused. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Identifying chelators for metalloprotein inhibitors using a fragment-based approach.
J. Med. Chem. 54 , 591-602, (2011) Fragment-based lead design (FBLD) has been used to identify new metal-binding groups for metalloenzyme inhibitors. When screened at 1 mM, a chelator fragment library (CFL-1.1) of 96 compounds produced... |
|
|
Photoluminescence and thermoanalytical studies of complexes based on 5-Cl-8-hydroxyquinoline and calix[4]arene ligands.
Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 33(4) , 2213-20, (2013) A innovative 5-Cl-8-oxyquinolinepropoxycalix[4]arene ligand (2) have been prepared, exhibiting, at room temperature, blue fluorescent light emission and resulting in shift band to green fluorescent li... |
|
|
Poly(L-lactide) and poly(butylene succinate) immiscible blends: from electrospinning to biologically active materials.
Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 41 , 119-26, (2014) For the first time the preparation of defect-free fibers from immiscible blends of high molar mass poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and poly(butylene succinate) (PBS) in the whole range of the polyester weight... |
| 5-Chloro-8-hydroxy quinoline |
| 5-chloroquinolin-8-ol |
| 5-Chloroquinophenol |
| cloxiquine |
| 5-Chlorooxine |
| EINECS 204-978-1 |
| 5-Chloro-8-quinolinol |
| 5-Chloro-8-hydroxyquinoline |
| 5-Chloro-quinolin-8-ol |
| 8-Quinolinol, 5-chloro- |
| Dermofungin |
| quinolin-8-ol, 5-chloro- |
| 5-Chloro-8-oxyquinoline |
| MFCD00006788 |
| 5-Chloro-8-oxychinolin |
| cloxyquin |
| 5-CHLORO-8-HYDROXY-QUINOLINE |
 CAS#:130-26-7
CAS#:130-26-7 CAS#:1198-14-7
CAS#:1198-14-7 CAS#:27037-46-3
CAS#:27037-46-3 CAS#:56-81-5
CAS#:56-81-5 CAS#:95-85-2
CAS#:95-85-2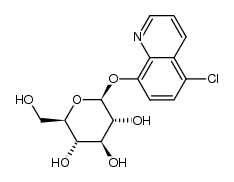 CAS#:101111-68-6
CAS#:101111-68-6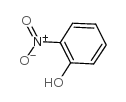 CAS#:88-75-5
CAS#:88-75-5 CAS#:10140-89-3
CAS#:10140-89-3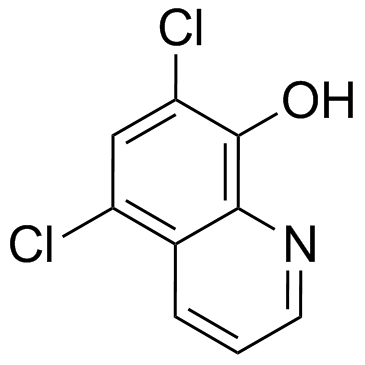 CAS#:773-76-2
CAS#:773-76-2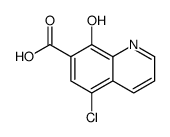 CAS#:205040-62-6
CAS#:205040-62-6 CAS#:18472-03-2
CAS#:18472-03-2 CAS#:99607-70-2
CAS#:99607-70-2 CAS#:7640-33-7
CAS#:7640-33-7 CAS#:100119-17-3
CAS#:100119-17-3 CAS#:103325-93-5
CAS#:103325-93-5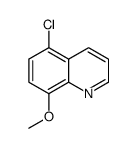 CAS#:17012-44-1
CAS#:17012-44-1 CAS#:157437-38-2
CAS#:157437-38-2 CAS#:114209-78-8
CAS#:114209-78-8
