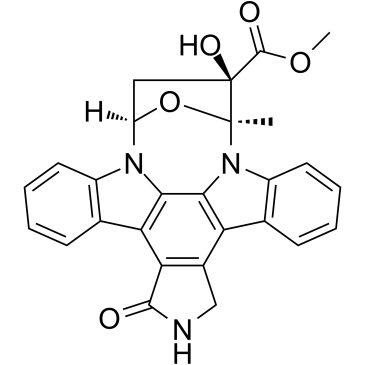
KT5823
KT5823 structure
|
Common Name | KT5823 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 126643-37-6 | Molecular Weight | 495.52600 | |
| Density | 1.52g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 629.2ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H25N3O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 334.3ºC | |
Use of KT5823KT5823, a selective the cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) inhibitor with an Ki value of 0.23 μM, it also inhibits PKA and PKC with Ki values of 10 μM and 4 μM, respectively[1]. KT5823 is a staurosporine-related protein kinase inhibitor, increases thyroid-stimulating hormone-induced (Na+/I- symporter) NIS expression, and iodide uptake in thyroid cells[2]. KT5823 arrests cells after the G0/G1 boundary and causes increases in the levels of apoptotic DNA fragmentation[3]. |
| Name | kt 5823 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | KT5823, a selective the cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) inhibitor with an Ki value of 0.23 μM, it also inhibits PKA and PKC with Ki values of 10 μM and 4 μM, respectively[1]. KT5823 is a staurosporine-related protein kinase inhibitor, increases thyroid-stimulating hormone-induced (Na+/I- symporter) NIS expression, and iodide uptake in thyroid cells[2]. KT5823 arrests cells after the G0/G1 boundary and causes increases in the levels of apoptotic DNA fragmentation[3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PKA:10 μM (Ki) PKC:4 μM (Ki) |
| References |
| Density | 1.52g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 629.2ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C29H25N3O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 495.52600 |
| Flash Point | 334.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 495.17900 |
| PSA | 74.93000 |
| LogP | 4.58930 |
| Vapour Pressure | 9.67E-16mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.763 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
~% 
KT5823 CAS#:126643-37-6 |
| Literature: Organic Process Research and Development, , vol. 3, # 2 p. 131 - 134 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Brain natriuretic peptide constitutively downregulates P2X3 receptors by controlling their phosphorylation state and membrane localization.
Mol. Pain 11 , 71, (2015) ATP-gated P2X3 receptors are important transducers of nociceptive stimuli and are almost exclusively expressed by sensory ganglion neurons. In mouse trigeminal ganglion (TG), P2X3 receptor function is... |
|
|
Interaction between bradykinin and natriuretic peptides via RGS protein activation in HEK-293 cells.
Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 303(12) , C1260-8, (2012) In this study, the interaction of natriuretic peptides (NP) and bradykinin (BK) signaling pathways was identified by measuring membrane potential (V(m)) and intracellular Ca(2+) using the patch-clamp ... |
|
|
Cytoprotective effect of 1-nitro-2-phenylethane in mice pancreatic acinar cells subjected to taurocholate: putative role of guanylyl cyclase-derived 8-nitro-cyclic-GMP.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 91(2) , 191-201, (2014) The nitroderivative 1-nitro-2-phenylethane (NPE) was recently described as a compound possessing heme-dependent soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) stimulating properties in vascular smooth muscle cells. I... |
| MFCD00132119 |
| (9S,10R,12R)-2,3,9,10,11,12-hexahydro-10-methoxy-2,9-dimethyl-1-oxo-9,12-epoxy-1H-diindolo[1,2,3-fg:3',2',1'-kl]pyrrolo[3,4-l][1,6]benzodiazocine-10-carboxylic acid methyl ester |