PHACLOFEN
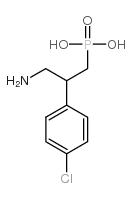
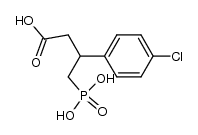
PHACLOFEN structure
|
Common Name | PHACLOFEN | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 114012-12-3 | Molecular Weight | 249.63100 | |
| Density | 1.432 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 467.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H13ClNO3P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 236.3ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of PHACLOFENPhaclofen is a selective GABAB receptor antagonist. Phaclofen is a peripheral and central baclofen antagonist. Phaclofen maybe a potential compound in determining the physiological significance of central and peripheral bicuculline-insensitive receptors with which GABA and (-)-baclofen interact[1][2]. |
| Name | Phaclofen,(RS)-3-Amino-2-(4-chlorophenyl)propylphosphonicacid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Phaclofen is a selective GABAB receptor antagonist. Phaclofen is a peripheral and central baclofen antagonist. Phaclofen maybe a potential compound in determining the physiological significance of central and peripheral bicuculline-insensitive receptors with which GABA and (-)-baclofen interact[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
GABAB receptor[1] |
| In Vivo | Phaclofen (100 nmol; intrathecal injection) antagonizes the depressant effect of baclofen. Phaclofen (100 nmol) is devoid of stimulatory or depressant effects on spinal reflexes[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.432 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 467.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C9H13ClNO3P |
| Molecular Weight | 249.63100 |
| Flash Point | 236.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 249.03200 |
| PSA | 93.36000 |
| LogP | 2.26030 |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
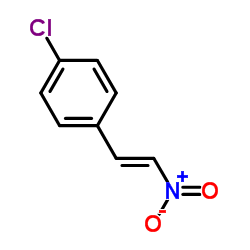
~% 
PHACLOFEN CAS#:114012-12-3 |
| Literature: Hall Synthesis, 1989 , # 6 p. 442 - 443 |
|
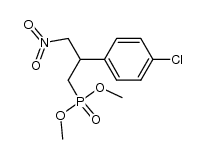
~% 
PHACLOFEN CAS#:114012-12-3 |
| Literature: Hall Synthesis, 1989 , # 6 p. 442 - 443 |
|
~% 
PHACLOFEN CAS#:114012-12-3 |
| Literature: Chiefari, John; Galanopoulos, Speros; Janowski, Wit K.; Kerr, David I. B.; Prager, Rolf H. Australian Journal of Chemistry, 1987 , vol. 40, # 9 p. 1511 - 1518 |
|
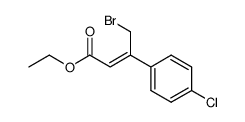
~% 
PHACLOFEN CAS#:114012-12-3 |
| Literature: Chiefari, John; Galanopoulos, Speros; Janowski, Wit K.; Kerr, David I. B.; Prager, Rolf H. Australian Journal of Chemistry, 1987 , vol. 40, # 9 p. 1511 - 1518 |
|
~% 
PHACLOFEN CAS#:114012-12-3 |
| Literature: Chiefari, John; Galanopoulos, Speros; Janowski, Wit K.; Kerr, David I. B.; Prager, Rolf H. Australian Journal of Chemistry, 1987 , vol. 40, # 9 p. 1511 - 1518 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
PKC-mediated GABAergic enhancement of dopaminergic responses: implication for short-term potentiation at a dual-transmitter synapse.
J. Neurophysiol. 112(1) , 22-9, (2014) Transmitter-mediated homosynaptic potentiation is generally implemented by the same transmitter that mediates the excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs), e.g., glutamate. When a presynaptic neuron... |
|
|
Transcriptome analysis of the key role of GAT2 gene in the hyper-accumulation of copper in the oyster Crassostrea angulata.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 17751, (2015) One paradigm of oysters as the hyper-accumulators of many toxic metals is the inter-individual variation of metals, but the molecular mechanisms remain very elusive. A comprehensive analysis of the tr... |
|
|
The antinociceptive effect of stimulating the retrosplenial cortex in the rat tail-flick test but not in the formalin test involves the rostral anterior cingulate cortex.
Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 131 , 112-8, (2015) The stimulation of the retrosplenial cortex (RSC) is antinociceptive in the rat tail-flick and formalin tests. The rat RSC is caudal to and send projections to the ipsilateral anterior cingulate corte... |
| 3-Amino-2-(4-chlorophenyl)propanephosphonic acid |
| MFCD00069328 |