Imipramine hydrochloride
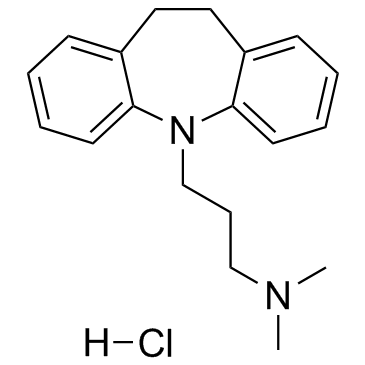
Imipramine hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Imipramine hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 113-52-0 | Molecular Weight | 316.868 | |
| Density | 1.041g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 403.1ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H25ClN2 | Melting Point | 168-1700C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 179.7ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Imipramine hydrochlorideImipramine hydrochloride inhibits serotonin transporter with an IC50 value of 32 nM in vitro. |
| Name | imipramine hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Imipramine hydrochloride inhibits serotonin transporter with an IC50 value of 32 nM in vitro. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 32 nM (serotonin)[1] |
| In Vitro | Depression-like behavior is often complicated by chronic pain. Antidepressants including imipramine are widely used to treat chronic pain, but the mechanisms are not fully understood[2]. Imipramine (IC50=32 nM) and desipramine (IC50=160 nM) are found to be potent inhibitors of the human placental serotonin transporter[1]. |
| In Vivo | Administration of imipramine reverses social avoidance behavior, significantly increasing the interaction time. 24 days of imipramine treatment in RSD mice significantly decreases stress-induced mRNA levels for IL-6 in brain microglia[3]. Chronic mild stress induces a long-term altered gene expression profile in the prefrontal cortex that is partially reverted by imipramine treatment (10mg/kg, i.p.)[4]. Chronic imipramine administration alteres the amino acid dynamics in the brain. In the striatum, the concentrations of asparagine, glutamine and methionine are significantly increased by chronic imipramine administration. In the thalamus and hypothalamus, chronic imipramine administration significantly decreased the valine concentration[5]. Imipramine reduces pain-related negative emotion without influencing pain and that this effect is diminished by denervation of 5-HT neurons and by anti-BDNF treatment. Imipramine also normalizes derangement of ERK/CREB coupling, which leads to induction of BDNF. This suggests a possible interaction between 5-HT and BDNF[2]. Imipramine treatment counteracts the corticosterone administration-induced increase in the reactivity of rat CA3 hippocampal circuitry to the activation of the 5-HT receptor[6]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: The Wistar (WIS) and Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rats are divided into four groups: (1) a control WIS rat group, (2) an imipramine-treated WIS rat group, (3) a control WKY rat group and (4) an imipramine-treated WKY rat group. Distilled water (10 mL/kg) or imipramine solution (10 mg/10 mL/kg) is orally administered for 28 days except on the day of the open field test, when nothing is administered in order to avoid the acute effect of single administration on the open field test[5]. Mice: C57BL/6 mice subjected to repeated social defeat (RSD), home cage control (HCC) are randomLy selected into four groups: RSD/imipramine, RSD/vehicle, HCC/imipramine, and HCC/vehicle. Mice in the RSD/imipramine received daily intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of imipramine (20 mg/kg) for 24 days after the 6 cycles of RSD. HCC/imipramine received daily i.p. imipramine at the same dose while RSD/vehicle and HCC/vehicle groups received i.p. injections of vehicle (sodium chloride, 0.9%) for 24 days at the same time point[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.041g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 403.1ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 168-1700C |
| Molecular Formula | C19H25ClN2 |
| Molecular Weight | 316.868 |
| Flash Point | 179.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 316.170624 |
| PSA | 6.48000 |
| LogP | 4.74200 |
| Appearance of Characters | crystalline | white |
| Vapour Pressure | 6.6E-06mmHg at 25°C |
| InChIKey | XZZXIYZZBJDEEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CN(C)CCCN1c2ccccc2CCc2ccccc21.Cl |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R23/25 |
| Safety Phrases | 7-16-24-33-45-36-26 |
| RIDADR | UN 1230 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | HO1925000 |
|
Antidepressants activate the lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA(1) to induce insulin-like growth factor-I receptor transactivation, stimulation of ERK1/2 signaling and cell proliferation in CHO-K1 fibroblasts.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 95 , 311-23, (2015) Different lines of evidence indicate that the lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptor LPA1 is involved in neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity and anxiety-related behavior, but little is known on whether th... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals ... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predicti... |
| Janimine (hydrochloride) |
| 3-(10,11-Dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepin-5-yl)-N,N-dimethyl-1-propanamine hydrochloride (1:1) |
| 5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine-5-propanamine, 10,11-dihydro-N,N-dimethyl-, monohydrochloride |
| 3-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepin-5-yl)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine hydrochloride |
| Imipramine hydrochloride |
| MFCD00012669 |
| EINECS 204-030-7 |
| 5H-Dibenz[b,f]azepine, 5-[3- (dimethylamino)propyl]-10,11-dihydro-, monohydrochloride |
| 3-(10,11-Dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepin-5-yl)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-aminhydrochlorid |
| Melipramine hydrochloride |
| Melipramine HCl |
| 3-(10,11-Dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepin-5-yl)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine hydrochloride (1:1) |
| N-(γ-Dimethylaminopropyl)iminodibenzyl hydrochloride |
| 3-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,f]azépin-5-yl)-N,N-diméthylpropan-1-amine chlorhydrate |
| Tofranil (hydrochloride) |
| 5H-Dibenz[b,f]azepine-5-propanamine, 10,11-dihydro-N,N-dimethyl-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Imipraminehydrochloride |
| Imipramine (hydrochloride) |
 CAS#:494-19-9
CAS#:494-19-9![3-(5,6-dihydrobenzo[b][1]benzazepin-11-yl)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine oxide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/457/6829-98-7.png) CAS#:6829-98-7
CAS#:6829-98-7 CAS#:50-47-5
CAS#:50-47-5 CAS#:796-28-1
CAS#:796-28-1![11-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-5,6-dihydrobenzo[b][1]benzazepin-3-ol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/327/303-70-8.png) CAS#:303-70-8
CAS#:303-70-8 CAS#:10075-24-8
CAS#:10075-24-8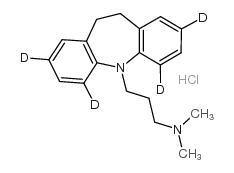 CAS#:61361-33-9
CAS#:61361-33-9
