N,N-Dimethylglycine

N,N-Dimethylglycine structure
|
Common Name | N,N-Dimethylglycine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1118-68-9 | Molecular Weight | 103.120 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 175.2±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H9NO2 | Melting Point | 178-182 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 59.8±22.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of N,N-DimethylglycineN-Methylsarcosine is an amino acid building block for protein, found in a small amount in the body. |
| Name | N,N-dimethylglycine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N-Methylsarcosine is an amino acid building block for protein, found in a small amount in the body. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 175.2±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 178-182 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H9NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 103.120 |
| Flash Point | 59.8±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 103.063332 |
| PSA | 40.54000 |
| LogP | -0.30 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.6±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.449 |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | MB9865000 |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Improving the serum D-xylose test for the identification of patients with small intestinal malabsorption.
J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 33(1) , 36-40, (2001) D-Xylose absorption testing is a simple, low-cost method of screening for small intestinal malabsorption. The optimum method to measure D-xylose absorption (serum vs. urine testing) is uncertain.We pr... |
|
|
Detection of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease by NMR spectroscopic fingerprinting of urine.
Kidney Int. 79(11) , 1244-53, (2011) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a frequent cause of kidney failure; however, urinary biomarkers for the disease are lacking. In a step towards identifying such markers, we used... |
|
|
Choline concentrations are lower in postnatal plasma of preterm infants than in cord plasma.
Eur. J. Nutr. 54 , 733-41, (2015) Choline is essential to human development, particularly of the brain in the form of phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin and acetylcholine, for bile and lipoprotein formation, and as a methyl group dona... |
| Glycine, N,N-dimethyl- |
| N-Methylsarcosine |
| N,N-Dimethylglycine |
| (Dimethylamino)acetic acid |
| N,N-dimethylaminoacetic acid |
| EINECS 214-267-8 |
| n,n-dimethyl-glycin |
| dimethylglycine |
| RARECHEM AL BO 0104 |
| dimethylaminoacetic acid |
| N,N-dimethyl-glycine |
| MFCD00004283 |
| Glycine,N,N-dimethyl |
| N-DiMethylglycine |
| 2-(Dimethylamino)acetic acid |
| N,N-Dimthylglycine |
| DMG |
 CAS#:50-00-0
CAS#:50-00-0 CAS#:56-40-6
CAS#:56-40-6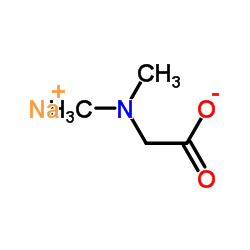 CAS#:18319-88-5
CAS#:18319-88-5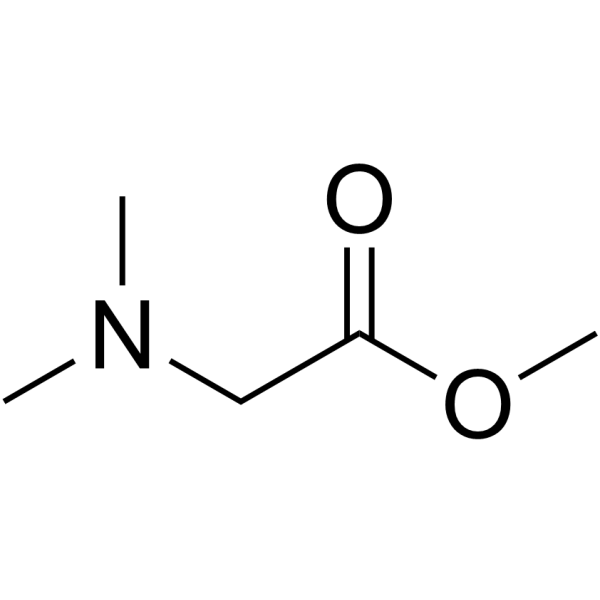 CAS#:7148-06-3
CAS#:7148-06-3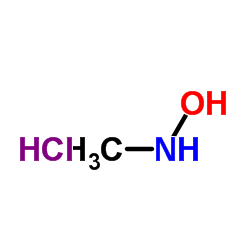 CAS#:4229-44-1
CAS#:4229-44-1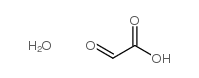 CAS#:6000-59-5
CAS#:6000-59-5 CAS#:124-40-3
CAS#:124-40-3 CAS#:298-12-4
CAS#:298-12-4 CAS#:79-11-8
CAS#:79-11-8 CAS#:33229-89-9
CAS#:33229-89-9 CAS#:348-67-4
CAS#:348-67-4 CAS#:26920-62-7
CAS#:26920-62-7 CAS#:127-19-5
CAS#:127-19-5![[Methyl(nitroso)amino]acetic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/268/13256-22-9.png) CAS#:13256-22-9
CAS#:13256-22-9 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9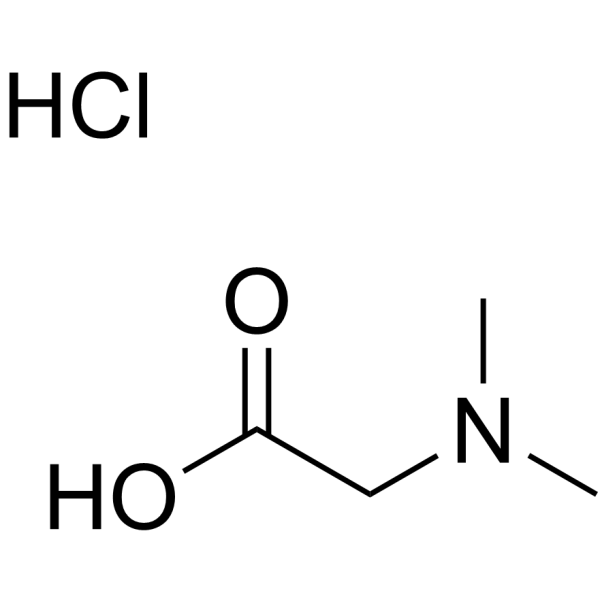 CAS#:2491-06-7
CAS#:2491-06-7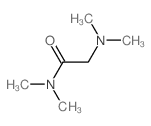 CAS#:13574-14-6
CAS#:13574-14-6
