1-Isocyanatobutane
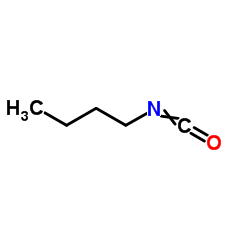
1-Isocyanatobutane structure
|
Common Name | 1-Isocyanatobutane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 111-36-4 | Molecular Weight | 99.131 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 115.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO | Melting Point | 85.5℃ | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 17.8±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |




GHS02, GHS05, GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | n-butyl isocyanate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 115.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 85.5℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO |
| Molecular Weight | 99.131 |
| Flash Point | 17.8±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 99.068413 |
| PSA | 29.43000 |
| LogP | 2.42 |
| Vapour density | 3 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 19.4±0.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.429 |
| InChIKey | HNHVTXYLRVGMHD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCN=C=O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |




GHS02, GHS05, GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H302-H311-H314-H330-H334 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P260-P280-P284-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;Goggles;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | F:Flammable |
| Risk Phrases | R11;R21/22;R26;R34;R37;R42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | S23-S26-S28-S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2485 6.1/PG 1 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | NQ8250000 |
| Packaging Group | I |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| HS Code | 2929109000 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2929109000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2929109000. other isocyanates. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
n-Butyl isocyanide oxidation at the [NiFe4S4OH(x)] cluster of CO dehydrogenase.
J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 17(2) , 167-73, (2012) Carbon monoxide dehydrogenases (CODHs) catalyze the reversible oxidation of carbon monoxide by reaction with water to yield carbon dioxide, two protons, and two electrons. Two principal types of CODHs... |
|
|
Assessing N,N'-Dibutylurea (DBU) formation in soils after application of n-butylisocyanate and benlate fungicides.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 52(4) , 747-54, (2004) N,N'-Dibutylurea (DBU) is a breakdown product of benomyl [methyl 1-(butylcarbamoyl)-2-benzimidazole carbamate], the active ingredient in Benlate fungicides, and has been proposed as one cause for crop... |
|
|
Butyl isocyanide as a probe of the activation mechanism of soluble guanylate cyclase. Investigating the role of non-heme nitric oxide.
J. Biol. Chem. 282(49) , 35741-8, (2007) Nitric oxide (NO) is a physiologically relevant activator of the hemoprotein soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC). In the presence of NO, sGC is activated several hundredfold above the basal level by a mec... |
| n-butyl isocynate |
| n-Butyl isocyanate |
| 1-Isocyanatobutane |
| 1-Butyl Isocyanate |
| Butylisocyanat |
| n-C4H9NCO |
| Butyl isocyanate |
| Isocyanic Acid Butyl Ester |
| EINECS 203-862-8 |
| n-bic |
| Butane, 1-isocyanato- |
| ISOCYANATOBUTANE |
| n-butyl isocyanante |
| butyl-isocyanate |
| BIC |
| MFCD00002046 |
 CAS#:29262-59-7
CAS#:29262-59-7 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9 CAS#:109-73-9
CAS#:109-73-9 CAS#:41891-17-2
CAS#:41891-17-2 CAS#:591-62-8
CAS#:591-62-8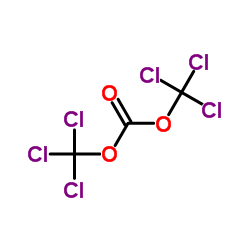 CAS#:32315-10-9
CAS#:32315-10-9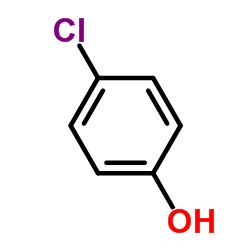 CAS#:106-48-9
CAS#:106-48-9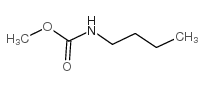 CAS#:2594-21-0
CAS#:2594-21-0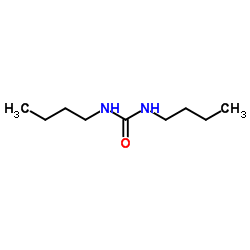 CAS#:1792-17-2
CAS#:1792-17-2 CAS#:75-44-5
CAS#:75-44-5 CAS#:105873-72-1
CAS#:105873-72-1 CAS#:105873-73-2
CAS#:105873-73-2 CAS#:339-43-5
CAS#:339-43-5 CAS#:141799-76-0
CAS#:141799-76-0 CAS#:143207-32-3
CAS#:143207-32-3 CAS#:1461-79-6
CAS#:1461-79-6![2,4-dibutyl-9-chlorobenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[4,3-a][1,3,5]triazine-1,3(2H,4H)-dione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/085/131581-74-3.png) CAS#:131581-74-3
CAS#:131581-74-3 CAS#:513-81-5
CAS#:513-81-5
