Diethylamine
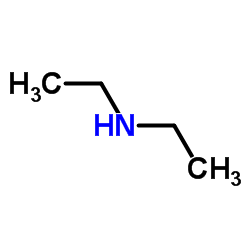
Diethylamine structure
|
Common Name | Diethylamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 109-89-7 | Molecular Weight | 73.137 | |
| Density | 0.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 57.3±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H11N | Melting Point | -50 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | -28.9±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | diethylamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 0.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 57.3±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -50 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C4H11N |
| Molecular Weight | 73.137 |
| Flash Point | -28.9±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 73.089149 |
| PSA | 12.03000 |
| LogP | 0.63 |
| Vapour density | 2.5 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 218.4±0.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.384 |
| InChIKey | HPNMFZURTQLUMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCNCC |
| Stability | Stable. Highly flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H302 + H332-H311-H314 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P280-P303 + P361 + P353-P304 + P340 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338-P370 + P378 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;Goggles;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US) |
| Hazard Codes | C:Corrosive |
| Risk Phrases | R11;R20/21/22;R35 |
| Safety Phrases | S16-S26-S29-S36/37/39-S45-S3 |
| RIDADR | UN 1154 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | HZ8750000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 3 |
| HS Code | 2921199090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2921199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2921199090 other acyclic monoamines and their derivatives; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Controlled Endolysosomal Release of Agents by pH-responsive Polymer Blend Particles.
Pharm. Res. 32 , 2280-91, (2015) A key step of delivering extracellular agents to its intracellular target is to escape from endosomal/lysosomal compartments, while minimizing the release of digestive enzymes that may compromise cell... |
|
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoret... |
|
|
Magnetic high throughput screening system for the development of nano-sized molecularly imprinted polymers for controlled delivery of curcumin.
Analyst 140(9) , 3113-20, (2015) Curcumin is a versatile anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer agent known for its low bioavailability, which could be improved by developing materials capable of binding and releasing drug in a controlled... |
| EINECS 203-716-3 |
| diphenyl-N,N-diethylcarbamoylmethylphosphine oxide |
| di-ethyl amine |
| Diethylamine |
| N,N-diethylamine |
| N-ethyl-ethanamine |
| MFCD00009032 |
| N-Ethylethanamine |
| Ceruletide diethylamine |
| Ethanamine, N-ethyl- |
| diphenylphosphinylacetic acid N,N-diethylamide |
| oxide of diphenyl<dibutylcarbamoylmethyl>phosphite |
 CAS#:75-04-7
CAS#:75-04-7 CAS#:75-07-0
CAS#:75-07-0 CAS#:64882-07-1
CAS#:64882-07-1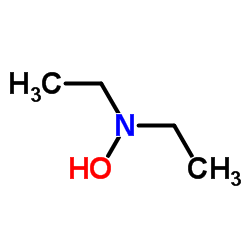 CAS#:3710-84-7
CAS#:3710-84-7 CAS#:54509-73-8
CAS#:54509-73-8 CAS#:64-17-5
CAS#:64-17-5 CAS#:75-05-8
CAS#:75-05-8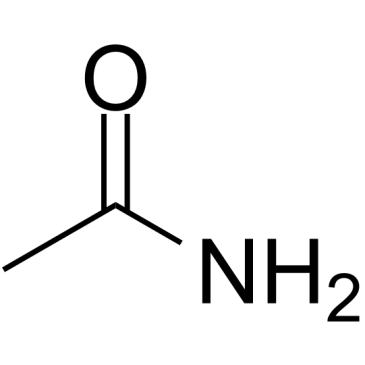 CAS#:60-35-5
CAS#:60-35-5 CAS#:849107-19-3
CAS#:849107-19-3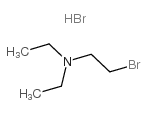 CAS#:1069-72-3
CAS#:1069-72-3![2-(prop-2-enylcarbamothioylamino)-N-[2-[[2-(prop-2-enylcarbamothioylamino)acetyl]amino]ethyl]acetamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/327/111915-68-5.png) CAS#:111915-68-5
CAS#:111915-68-5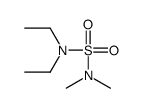 CAS#:106251-06-3
CAS#:106251-06-3 CAS#:10575-26-5
CAS#:10575-26-5 CAS#:111697-06-4
CAS#:111697-06-4 CAS#:112165-10-3
CAS#:112165-10-3 CAS#:103896-68-0
CAS#:103896-68-0 CAS#:91083-82-8
CAS#:91083-82-8 CAS#:10385-08-7
CAS#:10385-08-7 CAS#:111409-75-7
CAS#:111409-75-7 CAS#:111409-74-6
CAS#:111409-74-6
