H-DL-Orn-OH.HCl
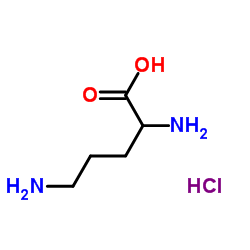
H-DL-Orn-OH.HCl structure
|
Common Name | H-DL-Orn-OH.HCl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1069-31-4 | Molecular Weight | 168.622 | |
| Density | 1.165 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 308.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H13ClN2O2 | Melting Point | 291ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 140.5ºC | |
| Name | DL-Ornithine Hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.165 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 308.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 291ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C5H13ClN2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 168.622 |
| Flash Point | 140.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 168.066559 |
| PSA | 89.34000 |
| LogP | 1.33980 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.00015mmHg at 25°C |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
|
~87% 
H-DL-Orn-OH.HCl CAS#:1069-31-4 |
| Literature: Prabhakaran; Woo; Yorgey; Gould Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1988 , vol. 110, # 17 p. 5785 - 5791 |
|
~60% 
H-DL-Orn-OH.HCl CAS#:1069-31-4 |
| Literature: Martinkus; Tann; Gould Tetrahedron, 1983 , vol. 39, # 21 p. 3493 - 3505 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Increased ornithine-derived polyamines cause airway hyperresponsiveness in a mouse model of asthma.
Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 48(6) , 694-702, (2013) Up-regulation of arginase contributes to airways hyperresponsiveness (AHR) in asthma by reducing L-arginine bioavailability for the nitric oxide (NO) synthase isozymes. The product of arginase activit... |
|
|
Microbacterium kyungheense sp. nov. and Microbacterium jejuense sp. nov., isolated from salty soil.
Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64(Pt 7) , 2267-73, (2014) Two novel strains, THG-C26(T) and THG-C31(T), were characterized using a polyphasic approach to determine their taxonomic positions. These two isolates were aerobic, Gram-stain-positive, non-motile, n... |
|
|
Disturbance of redox homeostasis by ornithine and homocitrulline in rat cerebellum: a possible mechanism of cerebellar dysfunction in HHH syndrome.
Life Sci. 93(4) , 161-8, (2013) Cerebellar ataxia is commonly observed in hyperornithinemia-hyperammonemia-homocitrullinuria (HHH) syndrome, an inherited metabolic disorder biochemically characterized by ornithine (Orn), homocitrull... |
| DL-Ornithinemonohydrochloride |
| L-Ornithine, monohydrochloride |
| DL-Ornithine Monohydrochloride |
| Ornithine, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| 2,5-diaminopentanoic acid,hydrochloride |
| MFCD00065398 |
| L-Ornithine hydrochloride (1:1) |
| (2S)-2,5-diaminopentanoic acid hydrochloride |
| Ornithine hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Z3YZVQ &&L or S Form HCl |
| Ornithine hydrochloride (VAN) |
| (S)-(+)-2,5-Diaminopentanoic acid hydrochloride |
| 2,5-Diaminopentanoic Acid Monohydrochloride |
| H-DL-Orn-OH·HCl |
| DL-Ornithine hydrochloride |
| Ornithine, monohydrochloride |
| L-Ornithine, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| ornithine monohydrochloride |
| 2,5-Diaminovaleric Acid Monohydrochloride |
| (S)-2,5-Diaminopentanoic acid monohydrochloride |
| EINECS 213-956-0 |
| L-ornithine hydrochloride |
| H-DL-Orn-OH.HCl |
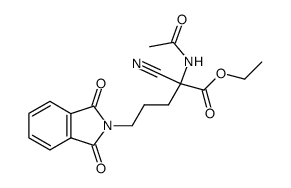


 CAS#:31967-09-6
CAS#:31967-09-6 CAS#:34294-79-6
CAS#:34294-79-6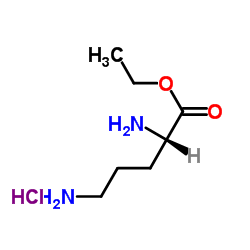 CAS#:84772-29-2
CAS#:84772-29-2 CAS#:83948-53-2
CAS#:83948-53-2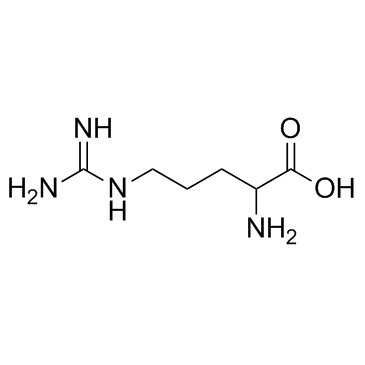 CAS#:7200-25-1
CAS#:7200-25-1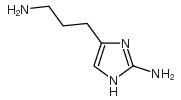 CAS#:202391-71-7
CAS#:202391-71-7 CAS#:1892-22-4
CAS#:1892-22-4 CAS#:56-12-2
CAS#:56-12-2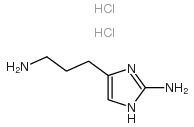 CAS#:80822-62-4
CAS#:80822-62-4 CAS#:84772-30-5
CAS#:84772-30-5
