N-Ethylaniline
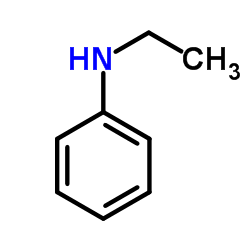
N-Ethylaniline structure
|
Common Name | N-Ethylaniline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 103-69-5 | Molecular Weight | 121.180 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 201.7±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H11N | Melting Point | -63 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 85.0±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | N-Ethylaniline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 201.7±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -63 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C8H11N |
| Molecular Weight | 121.180 |
| Flash Point | 85.0±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 121.089149 |
| PSA | 12.03000 |
| LogP | 2.13 |
| Vapour density | 4.2 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.3±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.559 |
| InChIKey | OJGMBLNIHDZDGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCNc1ccccc1 |
| Stability | Stable, but decomposes upon prolonged exposure to air or light. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. May react violently with nitric acid. |
| Water Solubility | 50 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H311-H331-H373 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P301 + P310-P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Phrases | R23/24/25:Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed . R33:Danger of cumulative effects. |
| Safety Phrases | S28-S37-S45-S28A |
| RIDADR | UN 2272 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | BX9780000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2921499090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2921420090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2921420090 aniline derivatives and their salts VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
cIEF for rapid pKa determination of small molecules: a proof of concept.
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 63 , 14-21, (2014) A capillary isoelectric focusing (cIEF) method was developed for the determination of the ionization constants (pKa) of small molecules. Two approaches used to decrease the electroosmotic flow (EOF) w... |
|
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoret... |
|
|
Spectroscopic studies of molecular interactions involving 2,6-diethylaniline and N-ethylaniline donors and iodine as an electron acceptor in different solvents.
Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 66(1) , 94-101, (2007) The charge-transfer complexes of 2,6-diethylaniline (DEA) and N-ethylaniline (NEA) with iodine, as a typical sigma-acceptor were studied spectrophotometrically in chloroform, dichloromethane and carbo... |
| N-Ethylaniline [UN2272] [Poison] |
| N-Ethyl-N-phenylamine |
| N-ethylbenzeneamine |
| Anilinoethane |
| EINECS 203-135-5 |
| aniline, N-ethyl- |
| Benzenamine, N-ethyl- |
| N-Ethylaniline |
| ANILINE,N-ETHYL |
| p-Ethylaminobenzene |
| Benzenamine,N-ethyl |
| N-Ethylaminobenzene |
| N-Ethylbenzenamine |
| N-monoethylaniline |
| MFCD00009025 |
| n-Ethyl aniline |
| Ethylaniline |
 CAS#:75-05-8
CAS#:75-05-8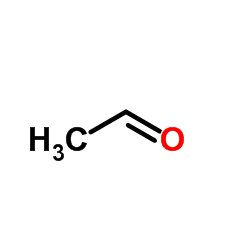 CAS#:75-07-0
CAS#:75-07-0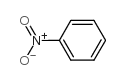 CAS#:98-95-3
CAS#:98-95-3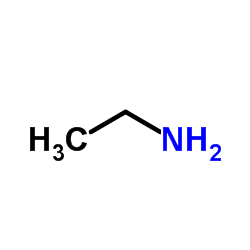 CAS#:75-04-7
CAS#:75-04-7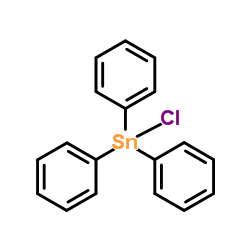 CAS#:639-58-7
CAS#:639-58-7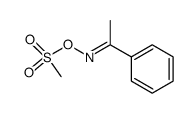 CAS#:85027-95-8
CAS#:85027-95-8 CAS#:696-18-4
CAS#:696-18-4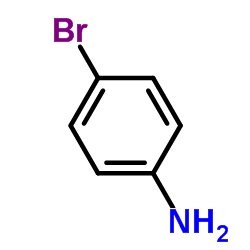 CAS#:106-40-1
CAS#:106-40-1 CAS#:56-81-5
CAS#:56-81-5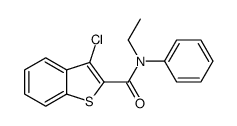 CAS#:105577-06-8
CAS#:105577-06-8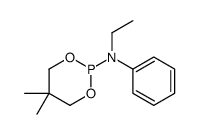 CAS#:111830-18-3
CAS#:111830-18-3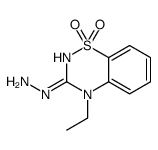 CAS#:107089-80-5
CAS#:107089-80-5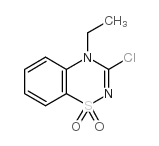 CAS#:107089-77-0
CAS#:107089-77-0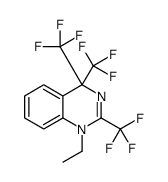 CAS#:106119-57-7
CAS#:106119-57-7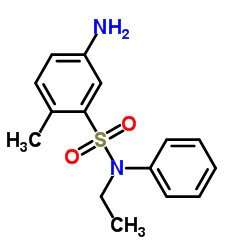 CAS#:51123-09-2
CAS#:51123-09-2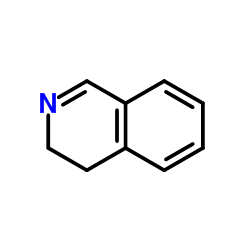 CAS#:3230-65-7
CAS#:3230-65-7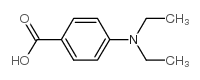 CAS#:5429-28-7
CAS#:5429-28-7 CAS#:3665-80-3
CAS#:3665-80-3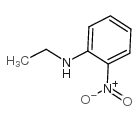 CAS#:10112-15-9
CAS#:10112-15-9
