Otenzepad
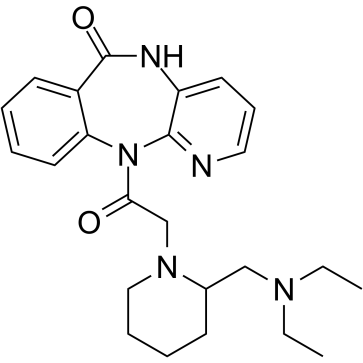
Otenzepad structure
|
Common Name | Otenzepad | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 102394-31-0 | Molecular Weight | 421.53500 | |
| Density | 1.171 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 573.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H31N5O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 300.5ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of OtenzepadOtenzepad (AF-DX 116) is a selective and competitive M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist, with IC50 values of 640 nM and 386 nM for rabbit peripheral lung and rat heart, respectively[1]. |
| Name | 11-[[2-[(Diethylamino)methyl]-1-piperidinyl]acetyl]-5,11-dihydro-6H-pyrido[2,3-b][1,4]benzodiazepin-6-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Otenzepad (AF-DX 116) is a selective and competitive M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist, with IC50 values of 640 nM and 386 nM for rabbit peripheral lung and rat heart, respectively[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
640 nM (M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in rabbit peripheral lung), 386 nM (M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in rat heart)[1]. |
| In Vivo | Otenzepad (0.5, 1 mg/kg, s.c., in rats) significantly improved win-stay acquisition relative to vehicle-injected controls[2]. Otenzepad (2 mg/kg, s.c., in rats) significantly improved retention relative to vehicle controls[2]. Otenzepad (0.3, 1.0, or 3.0 mg/kg, ip, in mice) potentiates the effects of glucose and reverses the effects of insulin on memory[3]. Animal Model: Forty-eight male Long-Evans rats (325-350 g)[2]. Dosage: 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 mg/kg. Administration: S.C. on the dorsum of the neck once. Result: Doses of 0.5 and 1.0 mg/kg significantly improved acquisition relative to vehicle controls, while doses of 0.25 and 2.0 mg/kg had no effect. Animal Model: Adult male Swiss mice (age 60–70 days; weight 25-30 g)[3]. Dosage: 0.3, 1.0, or 3.0 mg/kg. Administration: IP once. Result: Enhanced retention in an inverted-U dose–response manner, with significant enhancement seen at 1.0 mg/kg (U15,15 = 49, p < 0.02, compared with saline-saline-injected control group). |
| References |
| Density | 1.171 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 573.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C24H31N5O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 421.53500 |
| Flash Point | 300.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 421.24800 |
| PSA | 74.23000 |
| LogP | 3.21440 |
| InChIKey | UBRKDAVQCKZSPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCN(CC)CC1CCCCN1CC(=O)N1c2ccccc2C(=O)Nc2cccnc21 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Acetylcholine activity in selective striatal regions supports behavioral flexibility.
Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 91(1) , 13-22, (2009) Daily living often requires individuals to flexibly respond to new circumstances. There is considerable evidence that the striatum is part of a larger neural network that supports flexible adaptations... |
|
|
Nucleus accumbens acetylcholine and food intake: Decreased muscarinic tone reduces feeding but not food-seeking
Behav. Brain Res. 198(1) , 252-7, (2009) Separate groups of food-deprived rats were given 2 h access to food after receiving bilateral nucleus accumbens infusions of the muscarinic antagonist scopolamine methyl bromide (at 0, 1.0, and 10.0 μ... |
|
|
Loss of muscarinic and purinergic receptors in urinary bladder of rats with hydrochloric acid-induced cystitis.
Urology 76(4) , 1017.e7-12, (2010) To clarify the basic mechanism involved in the pathophysiology of cystitis by characterizing the urodynamic parameters, pharmacologically relevant (muscarinic and purinergic) receptors, and the in viv... |
| NPEC-caged-dopamine |
| ethyl)-7-piperidinyl)acetyl) |
| AF-DX 116 |
![5,11-Dihydro-11-chloroacetyl-6h-pyrido[2,3-b][1,4]benzodiazepine-6-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/041/28797-48-0.png) CAS#:28797-48-0
CAS#:28797-48-0![D,L-2-[(diethylamino)methyl]piperidine Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/152/100158-61-0.png) CAS#:100158-61-0
CAS#:100158-61-0![5,6-Dihydro-6-oxo-11H-pyrido[2,3-b][1,4]benzodiazepine Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/061/885-70-1.png) CAS#:885-70-1
CAS#:885-70-1