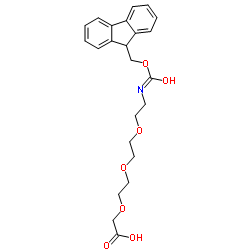
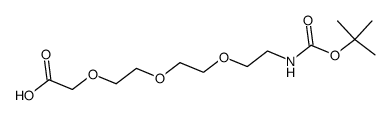
139338-72-0
| Name | (3E)-1-(9H-Fluoren-9-yl)-3-hydroxy-2,7,10,13-tetraoxa-4-azapentad ec-3-en-15-oic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
FMOC-PHE(3-OH)-OH
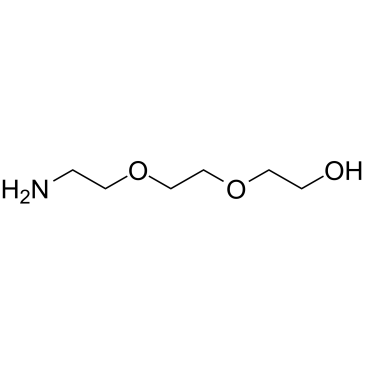
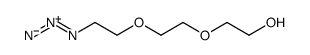
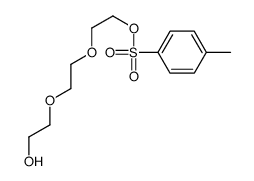
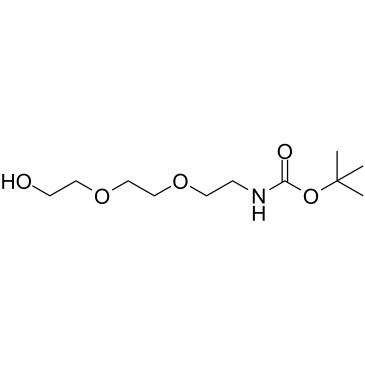
FMOC-L-M-TYR FMOC-3-HYDROXYL-L-PHENYLALANINE 2-{2-[2-(9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonylaminoethoxy)ethoxy]ethoxy}acetic acid Fmoc-D-phe(3-OH)-OH 1-(9H-Fluoren-9-yl)-3-oxo-2,7,10,13-tetraoxa-4-azapentadecan-15-oic acid Fmoc-3-hydroxy-L-Phe 11-(fluoren-9-ylmethyloxycarbonyl)amino-3,6,9-trioxaundecanoic acid (2-{2-[2-(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonylamino)ethoxy]ethoxy}ethoxy)acetic acid N-FMOC-3-HYDROXY-L-PHENYLALANINE Fmoc-meta-tyrosine Fmoc-11-amino-3,6,9-trioxaundecanoic acid Fmoc-Teg-OH Fmoc-PEG3-acetic acid 5,8,11-Trioxa-2-azatridecanedioic acid 1-(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethyl) ester |
| Description | Fmoc-amino-PEG3-CH2COOH is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PEGs Alkyl/ether |
| In Vitro | PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 651.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 46℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C23H27NO7 |
| Molecular Weight | 429.463 |
| Flash Point | 347.6±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 429.178741 |
| PSA | 106.81000 |
| LogP | 2.75 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.574 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |