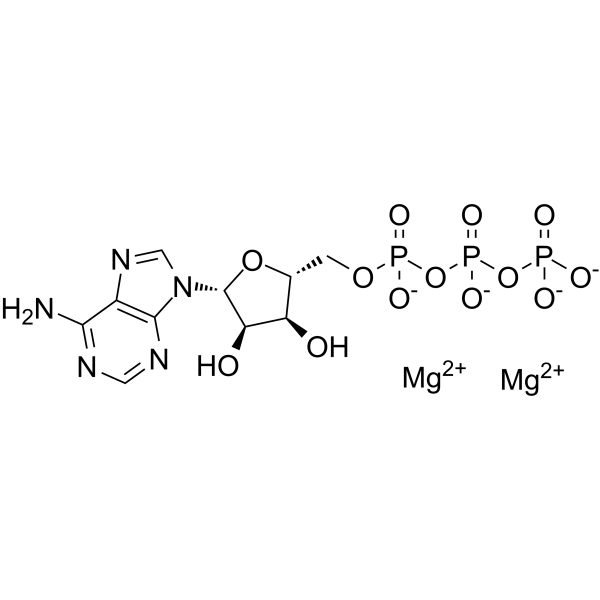
74804-12-9
| Name | [[5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] phosphono hydrogen phosphate,magnesium |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Adenosine 5'-triphosphate magnesium salt
ATP magnesium salt Adenosine 5 inverted exclamation marka-triphosphate magnesium salt ATP-MG |
| Description | ATP (Adenosine 5'-triphosphate) dimagnesium is a central component of energy storage and metabolism in vivo. ATP dimagnesium provides the metabolic energy to drive metabolic pumps and serves as a coenzyme in cells. ATP dimagnesium is an important endogenous signaling molecule in immunity and inflammation[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | ATP (5 mM; 1 hour) co-treatment with LPS (1 μg/mL) has a synergistic effect on the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in HGFs[3]. ATP (2 mM; 0.5-24 hours) induces secretion of IL-1β, KC and MIP-2 from BMDMs in a caspase-1 activation-dependent manner[4]. ATP promotes neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro[4]. |
| In Vivo | ATP (50 mg/kg; i.p.) protects mice against bacterial infection in vivo[4]. ATP induces the secretion of IL-1β, KC and MIP-2 and neutrophils recruitment in vivo[4]. Animal Model: Four-week-old Kunming mice (18-22 g)[4] Dosage: 50 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection, before bacterial (E. coli) challenge Result: Protected mice from bacterial infection. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C10H14MgN5O13P3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 529.47000 |
| Exact Mass | 528.96500 |
| PSA | 314.22000 |
| Storage condition | 20°C |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H371 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | 20/21/22-68/20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | 36/37 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |