19895-95-5
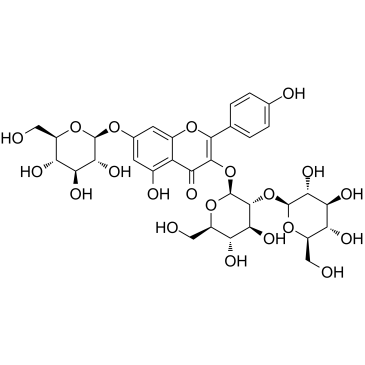
| Name | kaempferol 3-O-β-D-glucosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucoside |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranoside
Kaempferol-3-sophoroside Kaempferol 3-O-sophoroside Sophoraflavonoloside K3S 3-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chromen-4-one kaempferol 3-O-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside |
| Description | Kaempferol 3-O-sophoroside, a derivative of Kaempferol, is isolated from the leaves of cultivated mountain ginseng (Panax ginseng) with anti-inflammatory effects[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Kaempferol 3-O-sophoroside possesses barrier integrity activity, inhibitory activity on cell adhesion and migration to endothelial cells by blocking the activation of NF-κB expression and production of TNF-α, thereby endorsing its usefulness as therapy for vascular inflammatory diseases[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 995.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 194-198℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C27H30O16 |
| Molecular Weight | 610.518 |
| Flash Point | 329.3±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 610.153381 |
| PSA | 269.43000 |
| LogP | -0.58 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.764 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
|
~49% 
19895-95-5 |
| Literature: Markham, Kenneth R.; Andersen, Oeyvind M. Phytochemistry (Elsevier), 1990 , vol. 29, # 12 p. 3919 - 3920 |
|
~% 
19895-95-5 |
| Literature: Yoshida; Saito; Kadoya Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1987 , vol. 35, # 1 p. 97 - 107 |
|
~% 
19895-95-5 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 35, # 1 p. 97 - 107 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |