742-20-1
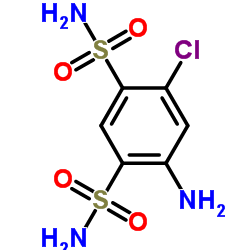
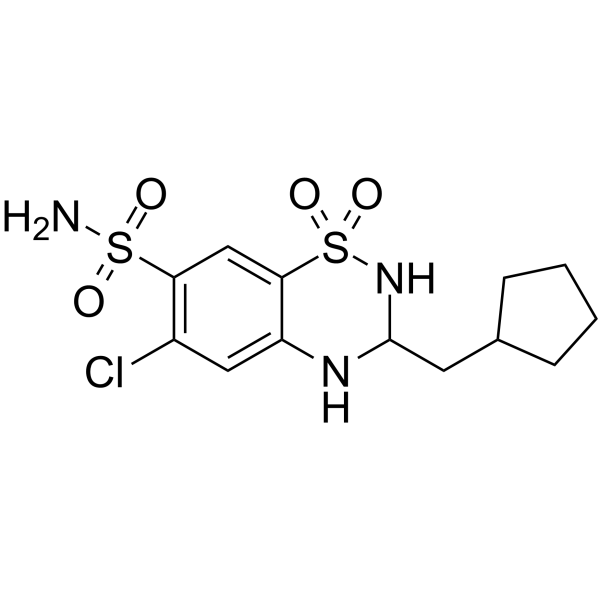
| Name | Cyclopenthiazide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
UNII:VX4S2N85F5
UNII:T7817XC41U EINECS 212-012-5 cyclopenthiazide 6-Chloro-3-cyclopentylmethyl-3,4-dihydro-7-sulfamoyl-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-Dioxide UNII:866GEV195O 6-chloro-3-(cyclopentylmethyl)-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1λ<sup>6</sup>,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 3-Cyclopentylmethyl-6-chloro-7-sulfamyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-Dioxide 6-Chloro-3-(cyclopentylmethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide Benesal (VAN) 2H-1,2,4-Benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(cyclopentylmethyl)-3,4-dihydro-, 1,1-dioxide MFCD00865825 Tsiklometiazid |
| Description | Cyclopenthiazide is a benzothiadiazine diuretic with antihypertensive properties. Cyclopenthiazide exerts a diuretic effect by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium chloride and water at the distal renal tubules. Cyclopenthiazide increases the excretory capacity of the rat kidney[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Cyclopenthiazide (0.5 mg/kg; i.p.; daily, for 3 days; female Wistar rats) increases the excretion of p-aminohippurate (PAH) [1]. Animal Model: Female Wistar rats[1] Dosage: 0.5 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; daily, for 3 days Result: Stimulated p-aminohippurate (PAH) excretion. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 605.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 238-242ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C13H18ClN3O4S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 379.883 |
| Flash Point | 320.1±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 379.042725 |
| PSA | 135.12000 |
| LogP | 1.58 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.601 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
|
~% 
742-20-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 26, p. 2814 - 2818 |
|
~% 
742-20-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 26, p. 2814 - 2818 |