1239262-52-2
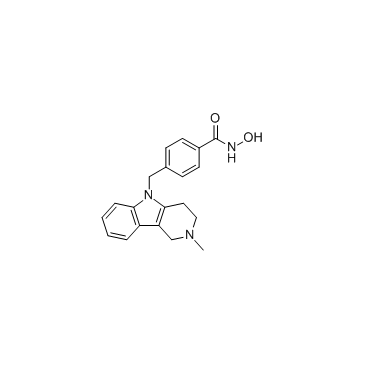
| Name | Tubastatin A Trifluoroacetate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
TUBASTATIN A HYDROCHLORIDE
N-hydroxy-4-({2-methyl-1H,3H,4H-pyrido[4,3-b]indol-5-yl}methyl)benzamide hydrochloride N-Hydroxy-4-[(2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-5H-pyrido[4,3-b]indol-5-yl)methyl]benzamide Tubastatin A Trifluoroacetic Acid Salt TUBASTSTINA HCL TUBASTATIN A ((2-METHYL-3,4-DIHYDRO-1H-PYRIDO[4,3-B]-INDOL- 5(2H)-YL)METHYL)BENZAMIDE) TUBASTATIN A_HCL Tubastatin A TUBASTANTIN A Tubastatin A (trifluoroacetate salt) TRIETHYLENETHIOPHOSPHORAMIDE,WHITE SOLID [4-({2-methyl-1H,2H,3H,4H,5H-pyrido[4,3-b]indol-5-yl}methyl)phenyl]formamido 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate N-Hydroxy-4-[(2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-5H-pyrido[4,3-b]indol-5 -yl)methyl]benzamide N-hydroxy-4-((2-methyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-pyrido[4,3-b]indol-5(2H)-yl)methyl)benzamide |
| Description | Tubastatin A (TSA) TFA is a potent and selective?HDAC6?inhibitor with?IC50?of 15 nM in a cell-free assay, and is selective (1000-fold more) against all other isozymes except HDAC8 (57-fold more). Tubastatin A TFA also inhibits HDAC10 and metallo-β-lactamase domain-containing protein?2 (MBLAC2). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 15 nM (HDAC6)[1] |
| In Vitro | Tubastatin A is substantially selective for all 11 HDAC isoforms and maintains over 1000-fold selectivity against all isoforms excluding HDAC8, where it has approximately 57-fold selectivity. In homocysteic acid (HCA) induced neurodegeneration assays, Tubastatin A displays dose-dependent protection against HCA-induced neuronal cell death starting at 5 μM with near complete protection at 10 μM[1].?At 100 ng/mL Tubastatin A increases Foxp3+ T-regulatory cells (Tregs) suppression of T cell proliferation in vitro[2].?Tubastatin A treatment in CC12 cells would lead to myotube formation impairment when alpha-tubulin is hyperacetylated early in the myogenic process; however, myotube elongation occurs when alpha-tubulin is hyeperacetylated in myotubes[3].?A recent study indicates that Tubastatin A treatment increases cell elasticity as revealed by atomic force microscopy (AFM) tests without exerting drastic changes to the actin microfilament or microtubule networks in mouse ovarian cancer cell lines, MOSE-E and MOSE-L[4]. |
| In Vivo | Daily treatment of Tubastatin A at 0.5 mg/kg inhibits HDAC6 to promote Tregs suppressive activity in mouse models of inflammation and autoimmunity, including multiple forms of experimental colitis and fully major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-incompatible cardiac allograft rejection[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H22F3N3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 449.42 |
| Exact Mass | 335.163391 |
| PSA | 94.80000 |
| LogP | 2.14 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.668 |
|
~31% 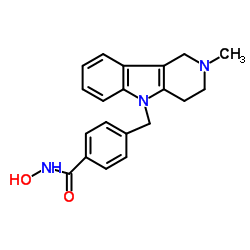
1239262-52-2 |
| Literature: THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS; KOZIKOWSKI, Alan; BUTLER, Kyle, B.; KALIN, Jay, Hans Patent: WO2011/11186 A2, 2011 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 54-55 ; WO 2011/011186 A2 |
|
~% 
1239262-52-2 |
| Literature: WO2011/11186 A2, ; WO 2011/011186 A2 |
|
~% 
1239262-52-2 |
| Literature: WO2011/11186 A2, ; WO 2011/011186 A2 |
|
~% 
1239262-52-2 |
| Literature: WO2011/11186 A2, ; WO 2011/011186 A2 |
|
~% 
1239262-52-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 132, # 31 p. 10842 - 10846 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |