27975-19-5
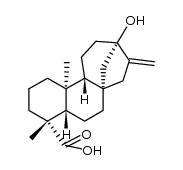
| Name | Isosteviol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
16-oxo-ent-beyeran-19-oic acid
iso-Steviol ent-16-oxobeyeran-19-oic acid 16-oxobeyeran-19-oic acid 16-Oxobeyeran-18-oic acid ent-16-ketobeyeran-19-oic acid |
| Description | Isosteviol is a derivative of stevioside, a constituent of Stevia rebaudiana, which is commonly used as a noncaloric sugar substitute in Japan and Brazil.Target:Isosteviol dose-dependently relaxed the vasopressin (10-8 M)-induced vasoconstriction in isolated aortic rings with or without endothelium. However, in the presence of potassium chloride (3×10-2 M), the vasodilator effect of isosteviol on arterial strips disappeared. Only the inhibitors specific for the ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel or small conductance calcium-activated potassium (SKCa) channel inhibited the vasodilator effect of isosteviol in isolated aortic rings contracted with 10-8 M vasopressin [1]. The attenuation by isosteviol of the vasopressin- and phenylephrine-induced increase in [Ca (2+)]i was inhibited by glibenclamide, apamin and 4-aminopyridine but not by charybdotoxin. Furthermore, the inhibitory action of isosteviol on [Ca (2+)]i was blocked when A7r5 cells co-treated with glibenclamide and apamin in conjunction with 4-aminopyridine were present [2]. Isosteviol (1-100 micromol/l) inhibits angiotensin-II-induced DNA synthesis and endothelin-1 secretion. Measurements of 2'7'-dichlorofluorescin diacetate, a redox-sensitive fluorescent dye, showed an isosteviol-mediated inhibition of intracellular reactive oxygen species generated by the effects of angiotensin II [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 455.6±38.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 228.0 to 232.0 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C20H30O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 318.450 |
| Flash Point | 243.5±23.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 318.219482 |
| PSA | 54.37000 |
| LogP | 4.13 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.551 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
~10% 
27975-19-5 |
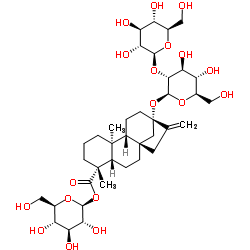
| Literature: Ukiya, Motohiko; Sawada, Shingo; Kikuchi, Takashi; Kushi, Yasunori; Fukatsu, Makoto; Akihisa, Toshihiro Chemistry and Biodiversity, 2013 , vol. 10, # 2 p. 177 - 188 |
|
~% 
27975-19-5 |
| Literature: Chaturvedula, Venkata Sai Prakash; Upreti, Mani; Prakash, Indra Molecules, 2011 , vol. 16, # 5 p. 3552 - 3562 |
|
~% 
27975-19-5 |
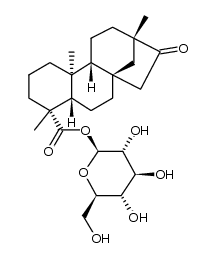
| Literature: Mosettig; Nes Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1955 , vol. 20, p. 884,895 Full Text Show Details Bridel; Lavieille Journal de Pharmacie et de Chimie, 1931 , vol. <8> 14, p. 321,325, 369, 372 Bulletin de la Societe de Chimie Biologique, 1931 , vol. 13, p. 781,785, 790 |
|
~% 
27975-19-5 |
| Literature: Bridel; Lavieille Journal de Pharmacie et de Chimie, 1931 , vol. <8> 14, p. 321,325, 369, 372 Bulletin de la Societe de Chimie Biologique, 1931 , vol. 13, p. 781,785, 790 |
|
~% 
27975-19-5 |
| Literature: Bridel; Lavieille Journal de Pharmacie et de Chimie, 1931 , vol. <8> 14, p. 99,100 Bulletin de la Societe de Chimie Biologique, 1931 , vol. 13, p. 636,645, 656 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |