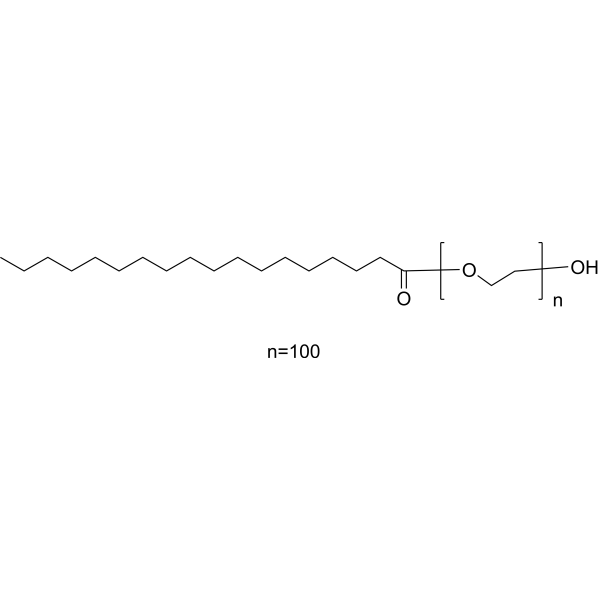
9004-99-3
| Name | Polyethylene Glycol Monostearate N-2 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ethylene glycol, monostearate
Stearic acid, 2-hydroxyethyl ester MFCD00151755 2-Hydroxyethyl octadecanoate 2-Hydroxyethyl stearate ETHYLENE GLYCOL MONOSTEARATE Octadecanoic acid, 2-hydroxyethyl ester Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), .α.-hydro-.ω.-hydroxy-, octadecanoate Polyoxyethylene stearate |
| Description | Polyoxyethylene stearate (POES) is a non-ionic emulsifying agent. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Polyoxyethylene stearate has been recommended as an additive to the radiolabelled 7H12 Middlebrook TB media and as such has been shown to enhance growth of mycobacteria in the radiometric BACTEC rapid culture system. Polyoxyethylene (50) stearate produces the greatest enhancement in growth and reduction in the time taken to detect growth for M. tuberculosis and polyoxyethylene (30) stearate and polyoxyethylene (JL) stearate for species of mycobacteria other than M. tuberculosis[1]. Polyoxyethylene stearate inhibits P-gp mediated efflux in a concentration dependent manner mainly by modulating substrate-stimulated P-gp ATPase activity[2]. Polyoxyethylene 40 stearate reduces vinblastine sulfate efllux. The cytotoxicity of vinblastine to K562/ADR cells is significantly enhanced when the cells are cotreated with 100 or 150 μg/mL polyoxyethylene 40 stearate[3]. |
| In Vivo | Polyoxyethylene stearate is potentially useful as a pharmaceutical ingredient to improve the oral bioavailability of coadministered P-gp substrates and substrates for certain CYP isoforms[2]. The average tumor volume and average tumor weight are significantly less in the polyoxyethylene 40 stearate+vinblastine group. The inhibition rate for tumor growth is increased from 0.06 (vinblastine group) to 0.84 (vinblastine+polyoxyethylene 40 stearate group)[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Polyoxyethylene 40 stearate is added to the test vinblastine solution. The cytotoxicity of vinblastine to K562/ADR cells is then assessed. The final concentrations of polyoxyethylene 40 stearate are 0, 50, 100, and 150 μg/mL. After 8 hours of treatment, cells are incubated for 4 hours in the presence of MTT reagent and then lysed with DMSO. Absorbance is measured at 490 nM[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: Polyoxyethylene 40 stearate and vinblastine are dissolved in 0.9% sodium chloride solution, yielding a solution of 200 μg/mL VBL and 150 μg/mL PS40. The drug is injected subcutaneously in a volume of 0.1 mL per 10 g of body weight at a dosage of 2 mg/kg vinblastine and 1.5 mg/kg polyoxyethylene 40 stearate around the tumor every other day for 8 days. The volume of tumors and the weight of mice are measured every day from the day the tumors are formed[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 438.4±18.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 47ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C20H40O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 328.530 |
| Flash Point | 164.6±14.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 328.297760 |
| PSA | 46.53000 |
| LogP | 7.85 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.457 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | MD0907300 |