1147299-69-1
| Name | Safinamide-d4 |
|---|
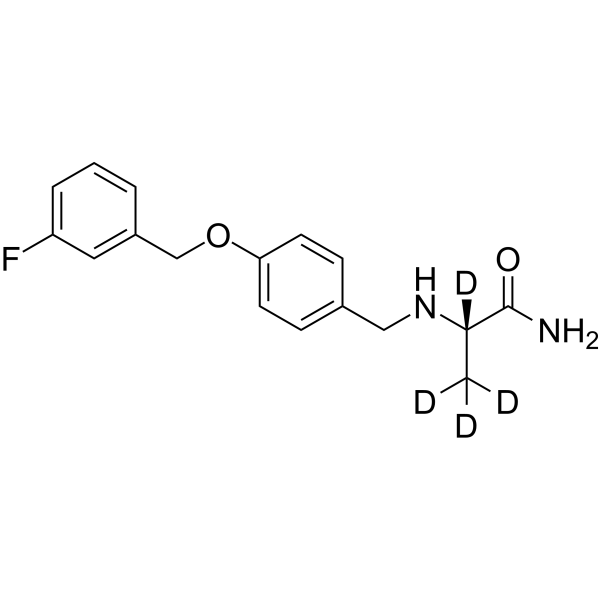
| Description | Safinamide-d4 (FCE 26743-d4) is the deuterium labeled Safinamide. Safinamide is a potent, selective, and reversible monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibitor (IC50=0.098 µM) over MAO-A (IC50=580 µM)[1]. Safinamide also blocks sodium channels and modulates glutamate (Glu) release, showing a greater affinity at depolarized (IC50=8 µM) than at resting (IC50=262 µM) potentials. Safinamide has neuroprotective and neurorescuing effects and can be used for the study of parkinson disease, ischemia stroke etc.al[2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C17H15D4FN2O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 306.37 |