107-35-7
| Name | Taurine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
EINECS 203-483-8
Taurine tauphon Taukard taurine zwitterion 2-aminoethanesulphonic acid b-Aminoethylsulfonic acid 2-aminoethane sulfonic acid TATU TURIN 2-aminoethylsulfonic acid 2-sulfoethylamine β-Aminoethylsulfonic acid O-Due FEMA 3813 Taufon MFCD00008197 2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid |
| Description | Taurine is an organic acid widely distributed in animal tissues.Target: OthersTaurine is a major constituent of bile and can be found in the large intestine and accounts for approximately 0.1% of total human body weight [1]. Taurine is present in high concentration in algae and in the animals including insects and arthropods, but is generally absent or present in traces in the bacterial and plant kingdoms [2]. In cardiac tissue alone, taurine levels of 20 mM or higher may be found. Taurine availability protects against cholestasis induced by monohydroxy bile acids remains confined to guinea pigs [3]. Oral supplementation of taurine results in increased plasma taurine concentrations and is associated with normalization of left ventricular function in both groups of cats. Myocardial concentrations of taurine are directly related to plasma concentrations and low plasma concentrations are found to be associated with myocardial failure in cats, proposing a direct link occurs between decreased taurine concentration in the myocardium and decreased myocardial mechanical function [4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
[1]. Huxtable, R.J., Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol Rev, 1992. 72(1): p. 101-63. |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) |
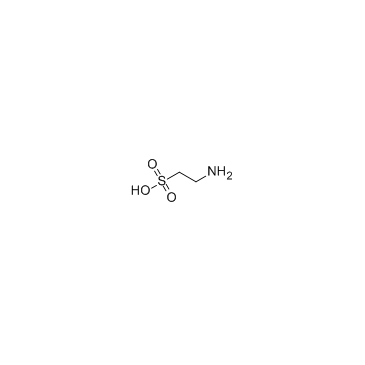
| Molecular Formula | C2H7NO3S |
| Molecular Weight | 125.147 |
| Exact Mass | 125.014664 |
| PSA | 88.77000 |
| LogP | -2.46 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.515 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | 5-10 g/100 mL at 23.5 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | WX0175000 |
| HS Code | 2921199090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2921199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2921199090 other acyclic monoamines and their derivatives; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |




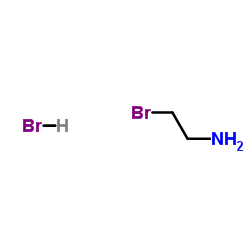

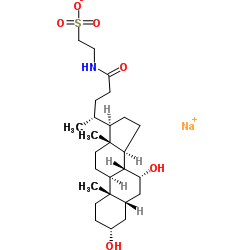
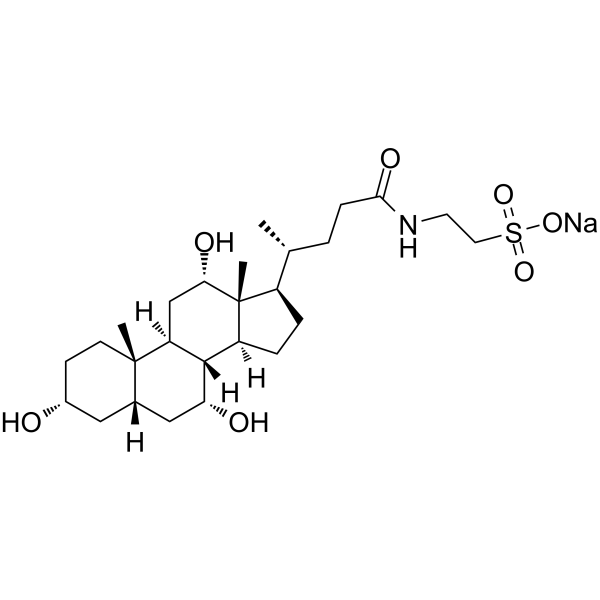
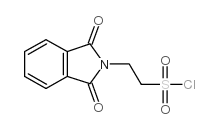



![2-(1-cyano-2H-benzo[f]isoindol-2-yl)ethanesulfonic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/158/110926-99-3.png)
