105990-27-0
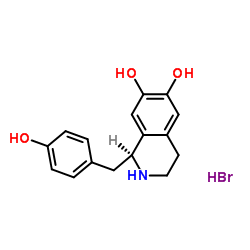
| Name | (1S)-1-(4-Hydroxybenzyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-isoquinolinediol hydrobromide (1:1) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
6,7-Isoquinolinediol, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-, (1S)-, hydrobromide (1:1)
(1S)-1-(4-Hydroxybenzyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-isoquinolinediol hydrobromide (1:1) |
| Description | (S)-Higenamine ((S)-Norcoclaurine) hydrobromide, a S-enantiomer of Higenamine, is the entry compound in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis. (S)-Higenamine hydrobromide is produced by the condensation of dopamine and 4-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (4-HPAA) by norcoclaurine synthase (NCS)[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | The biosynthetic pathway leading to benzylisoquinoline alkaloids originates from the enzyme-catalyzed condensation of dopamine and 4-hydrophenylacetaldehyde to yield (S)-norcoclaurine. Both substrates are secondary metabolites derived from the decarboxylation/hydroxylation/deamination of tyrosine[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C16H18BrNO3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 352.223 |
| Exact Mass | 351.046997 |