184475-56-7
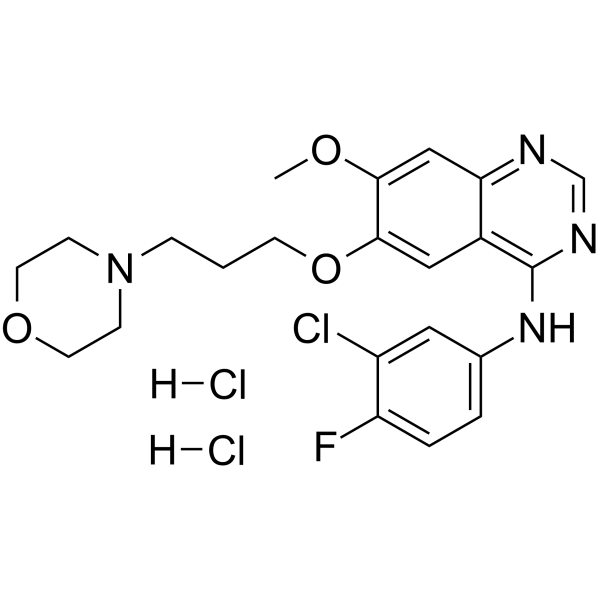
| Name | 4-(3-Chloro-4-fluorophenylamino)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy]quinazoline dihydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Gefitinib dihydrochloride
4-quinazolinamine, N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy]-, hydrochloride (1:2) N-(3-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(morpholin-4-yl)propoxy]quinazolin-4-amine dihydrochloride |
| Description | Gefitinib (ZD 1839) dihydrochloride is a potent, selective and orally active EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an IC50 of 33 nM. Gefitinib dihydrochloride selectively inhibits EGF-stimulated tumor cell growth (IC50 of 54 nM) and blocks EGF-stimulated EGFR autophosphorylation in tumor cells. Gefitinib dihydrochloride also induces autophagy and cell apoptosis, which can be used for cancer related research, such as Lung cancer and breast cancer [1][2][5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 37 nM (Tyr1173 site, in NR6wtEGFR cells), 37 nM (Tyr992 site, in NR6wtEGFR cells)[1]. |
| In Vitro | Gefitinib dihydrochloride (0.01–0.1 μM, 72 h) results in increased phosphotyrosine load of the receptor, increased signalling to ERK and stimulation of proliferation and anchorage-independent growth[2]. Gefitinib dihydrochloride (1-2 μM, 72 h) significantly decreases EGFRvIII phosphotyrosine load, EGFRvIII-mediated proliferation and anchorage-independent growth[2]. Gefitinib dihydrochloride (0.62 μM, 24-72 h) inhibits IL-13-induced M2-like polarization of RAW 264.7 cells through the STAT6-dependent signaling pathway[3]. Gefitinib dihydrochloride (0.62 μM, 72 h) inhibits M2-like macrophage-promoted invasion and migration[3]. Gefitinib dihydrochloride (0-10 μM, 72 h) induces apoptosis (induction of BIM protein) in NSCLC Cell Lines (H3255 and HCC827 cells)[4]. Western Blot Analysis[2] Cell Line: NR6wtEGFR, NR6W and NR6M Concentration: 1, 10, 100 μM Incubation Time: 5 h Result: Inhibited EGFR tyrosine phosphorylations. Cell Migration Assay [3] Cell Line: LLCs cell Concentration: 0.62 μM Incubation Time: 72 h Result: Abrogated M2-like macrophage promoted invasion and migration of LLCs. |
| In Vivo | Gefitinib dihydrochloride (Oral administration, 75 mg/kg/d, 21 days) inhibits the M2-like polarization of macrophages in LLC mice metastasis model[3]. Gefitinib dihydrochloride (Oral administration, 75 mg/kg for the initial week, daily for 5 consecutive days per week) eliminates phosphorylation of HER2 and HER3 and signaling through MAPK and Akt in lobular hyperplasias and carcinomas, increases MAPK activity and cytokine production in splenocytes and lymph nodes[5]. Animal Model: LLC mice metastasis model[3] Dosage: 75 mg/kg/d, for 21 days. Administration: Oral administration Result: Reduced the number of lung metastasis nodules, down-regulated the expression of M2 marker genes and the percentages CD206+ and CD68+ macrophages in tumor tissues. Animal Model: BALB-NeuT transgenic mouse model[5] Dosage: 75 mg/kg for the initial week, and increased by 15 mg/kg every other week, daily for 5 consecutive days per week, followed by 2 days without treatment and repeated for 8–9 weeks. Administration: Oral administration Result: Reduced tumor multiplicity from 9.6 to 0.58 (83%), and reduced the number and size of lobules and lobular nodules in treated mice. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 628.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H26Cl3FN4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 519.824 |
| Flash Point | 333.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 518.105469 |
| PSA | 68.74000 |
| LogP | 5.89050 |
| Vapour Pressure | 4.9E-16mmHg at 25°C |