| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ketoconazole
CAS:65277-42-1 |
|
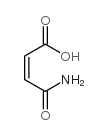 |
(Z)-4-Amino-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid
CAS:557-24-4 |
|
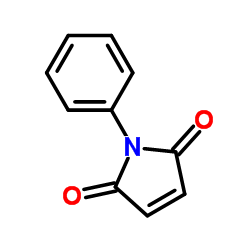 |
N-Phenylmaleimide
CAS:941-69-5 |