| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
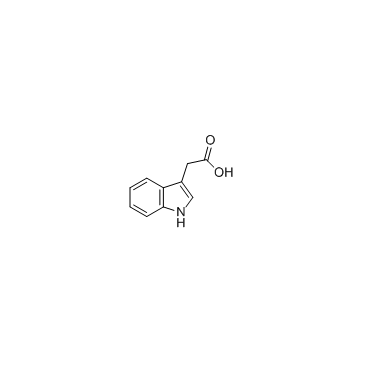 |
3-Indoleacetic acid
CAS:87-51-4 |
|
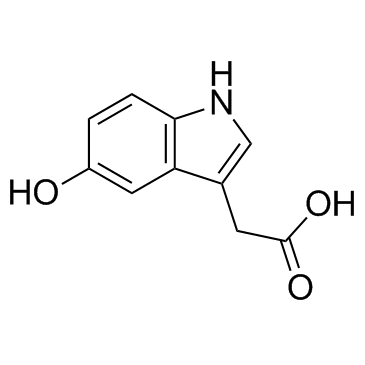 |
5-Hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid
CAS:54-16-0 |
|
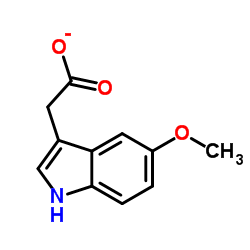 |
5-Methoxyindole-3-acetic acid
CAS:3471-31-6 |