| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
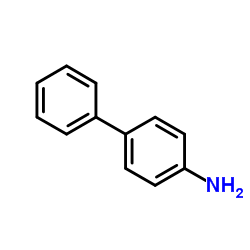 |
4-Aminobiphenyl
CAS:92-67-1 |
|
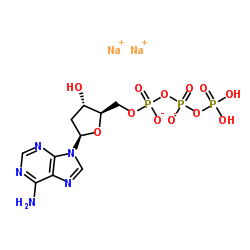 |
2'-Deoxyadenosine-5'-triphosphate
CAS:1927-31-7 |
|
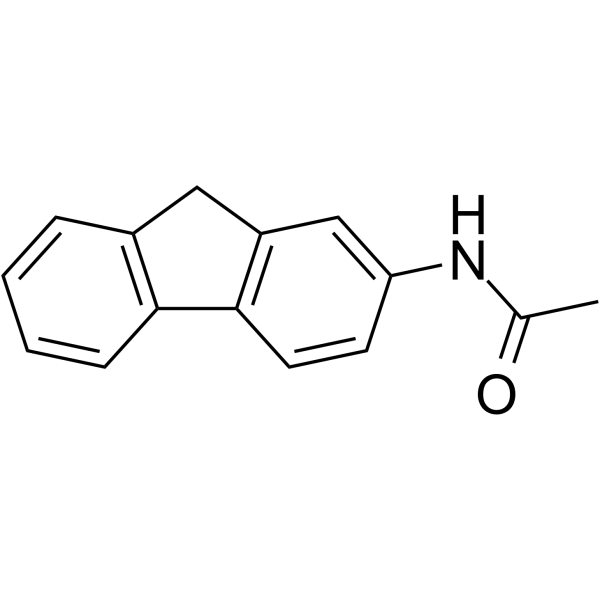 |
2-Acetamidofluorene
CAS:53-96-3 |
|
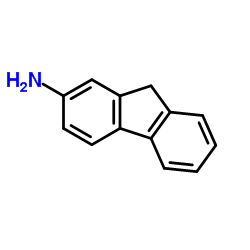 |
2-aminofluorene
CAS:153-78-6 |