| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
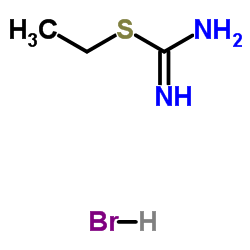 |
Ethyl carbamimidothioate hydrobromide (1:1)
CAS:1071-37-0 |
|
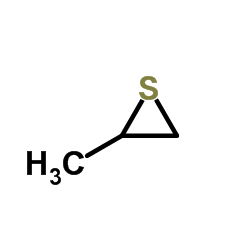 |
2-Methylthiirane
CAS:1072-43-1 |