Peroxidative activation of o-phenylhydroquinone leads to the formation of DNA adducts in HL-60 cells.
E Horvath, G Levay, K Pongracz, W J Bodell
Index: Carcinogenesis 13(10) , 1937-9, (1992)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Using 32P-postlabeling we studied DNA adduct formation in HL-60 cells treated with the o-phenylphenol metabolites o-phenylhydroquinone (o-PHQ) and o-phenylbenzoquinone (o-PBQ). Treatment with 25-500 microM o-PHQ for 8 h produced one principal and three minor adducts with a relative distribution of 80, 10, 6 and 4%. The relative adduct levels from these treatments were 0.26-2.31 adducts/10(7) nucleotides. Treatment with 25-250 microM o-PBQ for 2 h resulted in a similar level of DNA modification and adduct distribution. Reaction of purified calf thymus DNA with o-PBQ produced one DNA adduct, which did not correspond to the major adduct produced in HL-60 cells. These results show that o-PHQ and o-PBQ can form DNA adducts. Peroxidase activation of o-phenylphenol may therefore play a role in the carcinogenic effect of this compound.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
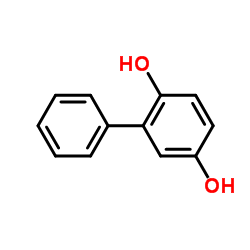 |
2,5-Biphenyldiol
CAS:1079-21-6 |
C12H10O2 |
|
Cytotoxic effects of phenyl-hydroquinone and some hydroquino...
1992-09-25 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 44(6) , 1059-65, (1992)] |
|
Tuning surface hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of hydrocarbon ...
2016-03-15 [J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 466 , 168-77, (2016)] |
|
Metabolism of phenylhydroquinone by prostaglandin (H) syntha...
1991-01-01 [Carcinogenesis 12(1) , 145-9, (1991)] |
|
The inhibition of phenylhydroquinone-induced oxidative DNA c...
2000-02-01 [Biol. Pharm. Bull. 23(2) , 199-203, (2000)] |
|
Metabolites of the biocide o-phenylphenol generate oxidative...
2000-01-01 [Arch. Toxicol. 73(10-11) , 607-10, (2000)] |