Metabolites of the biocide o-phenylphenol generate oxidative DNA lesions in V 79 cells.
P Henschke, E Almstadt, S Lüttgert, K E Appel
Index: Arch. Toxicol. 73(10-11) , 607-10, (2000)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Incubation of the o-phenylphenol (OPP) metabolites, o-phenylhydroquinone (PHQ) and o-phenylbenzoquinone (PBQ) with V 79 Chinese hamster cells led to a significant enhancement of the amount of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OH-dG) in nuclear DNA. With OPP no distinct induction of this lesion could be observed. In addition, PHQ and PBQ were able to generate DNA single-strand breaks (DNA SSB), while OPP failed to induce this lesion. All incubations were performed for 1 h without exogenous metabolic activations and the lowest effective concentration tested was 20 microM. It is concluded that these metabolites may contribute to the carcinogenicity of OPP and sodium o-phenylphenolate (SOPP) observed in rats, by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) through their redox cycling properties.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
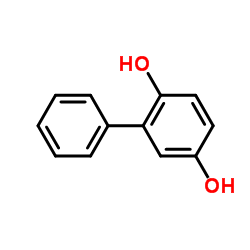 |
2,5-Biphenyldiol
CAS:1079-21-6 |
C12H10O2 |
|
Cytotoxic effects of phenyl-hydroquinone and some hydroquino...
1992-09-25 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 44(6) , 1059-65, (1992)] |
|
Tuning surface hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of hydrocarbon ...
2016-03-15 [J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 466 , 168-77, (2016)] |
|
Metabolism of phenylhydroquinone by prostaglandin (H) syntha...
1991-01-01 [Carcinogenesis 12(1) , 145-9, (1991)] |
|
The inhibition of phenylhydroquinone-induced oxidative DNA c...
2000-02-01 [Biol. Pharm. Bull. 23(2) , 199-203, (2000)] |
|
DNA adduct formation by o-phenylphenol metabolite in vivo an...
1992-08-01 [Carcinogenesis 13(8) , 1469-73, (1992)] |